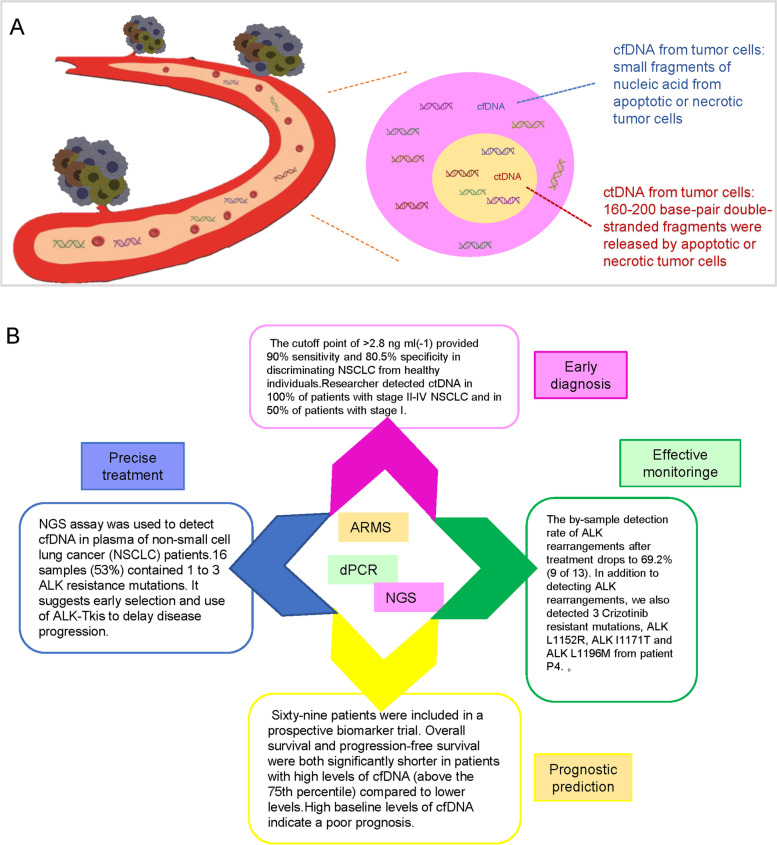
Fig. 4.
Clinical application and common detection techniques of ctDNA in lung cancer. A Circulating free DNA (cfDNA) from both normal and tumor cells is released via necrosis and apoptosis into the blood circulation. In cancer patients, a small portion of cfDNA is shed into the blood by tumor cells—this is called ctDNA. B ctDNA is cleared soon after entering the circulation due to its short half-life of 2 h, allowing for non-invasive real-time tumor monitoring. The implementation of ctDNA detection in clinical practice holds great potential for early detection and personalized medicine in lung cancer