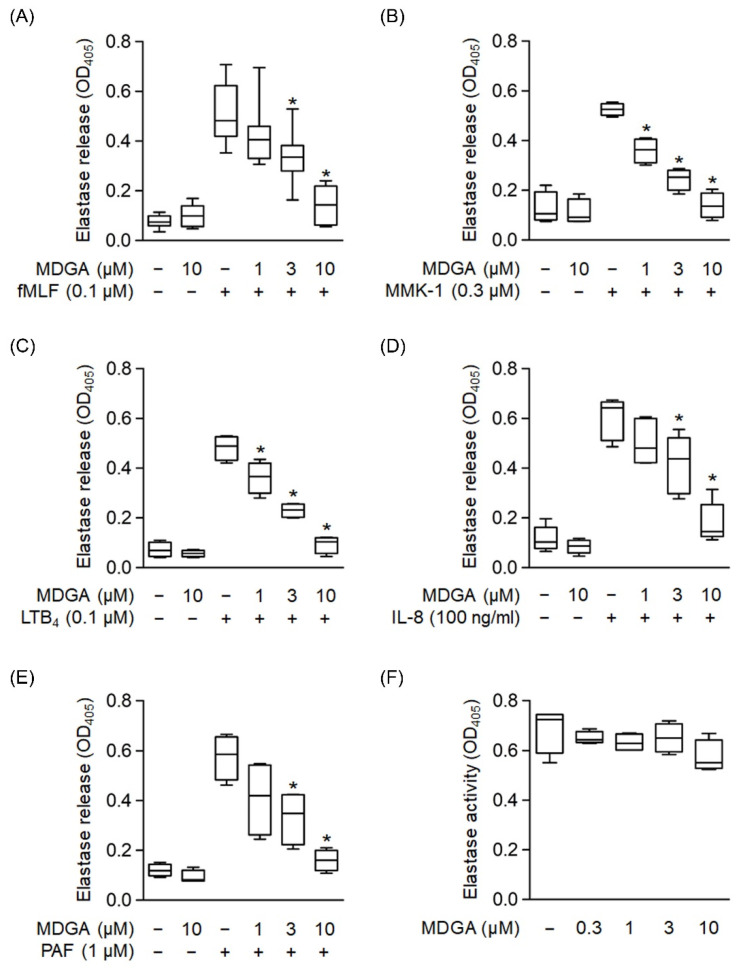
Figure 4.
meso-Dihydroguaiaretic acid (MDGA) suppresses elastase release from stimulated human neutrophils. Human neutrophils were prepared with DMSO (0.1%) or MDGA (1, 3, and 10 μM) and then activated by (A) fMLF (0.1 μM) + CB (0.5 μg/mL), (B) MMK-1 (0.3 μM) + CB (0.5 μg/mL), (C) leukotriene B4 (LTB4, 0.1 μM) + CB (0.5 μg/mL), (D) interleukin-8 (IL-8, 100 ng/mL) + CB (0.5 μg/mL), or (E) platelet-activating factor (PAF, 1 μM) + CB (0.5 μg/mL). Elastase release was measured spectrophotometrically at 405 nm. All data are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4–7). * p < 0.05 vs. stimulated control. (F) Human neutrophils were incubated with fMLF (0.1 μM) + CB (1.5 μg/mL) for 15 min. The elastase supernatant was obtained and then incubated with DMSO (0.1%) or MDGA (0.3–10 μM) for 2 min before the addition of substrate (100 μM). Elastase activity was measured spectrophotometrically at 405 nm. All data are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4).