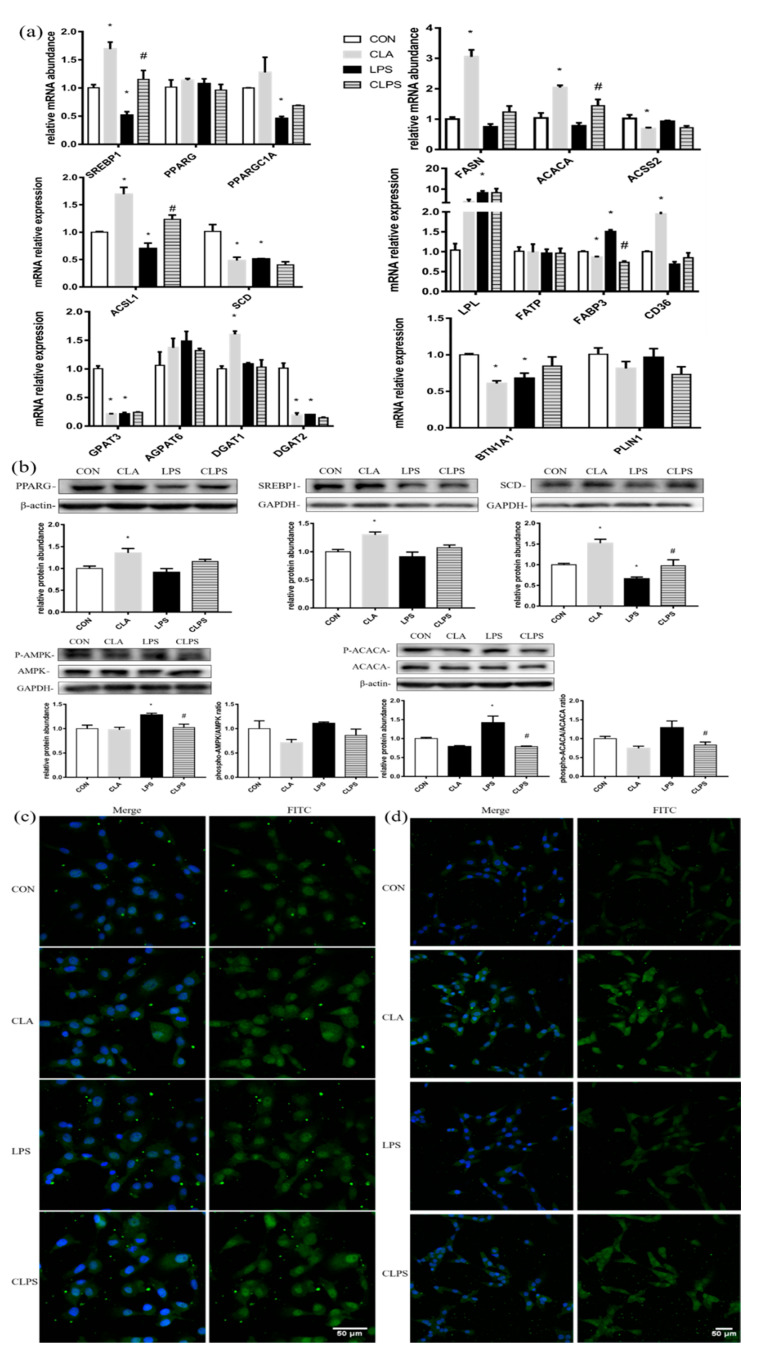
Figure 8.
CLA pretreatment relieved the depression of fatty acid synthesis induced by LPS challenge in BMECs. (a)The mRNA abundance of transcription factors (SREBP1, PPARG and PPARGC1A), de novo synthase (ACACA, FASN and ACSS2), long-chain fatty acid converting enzymes (ACSL1 and SCD), fatty acid transporters (CD36, LPL, FATP and FABP3), triglyceride synthase (GPAT3, AGPAT6, DGAT1 and DGAT2) and lipid droplet-releasing enzyme (BTN1A1 and PLIN1). (b) Immunoblotting of fatty acid synthesis-related transcription factors (SREBP1 and PPARG), enzymes (SCD and ACACA) and AMPK by Western blotting. (c) Immunofluorescence of PPARG and (d) SREBP1 stained with FITC fluorescence (green) were visualized by laser confocal microscopy. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). GAPDH was the housekeeping gene and GAPDH or β-actin was the reference proteins. The results are presented as means ± SEM. * p ≤ 0.05, significantly different from CON; # p ≤ 0.05, significantly different from LPS. Experiments were repeated three times independently with triplicates in each treatment.