Figure 3.
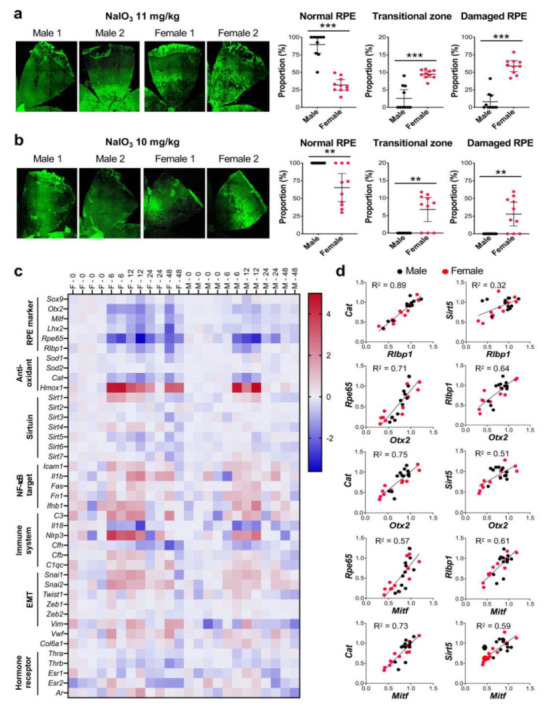
The RPE is more susceptible to NaIO3 in female mice than in male mice. (a,b) Sex-specific differences in the degree of RPE damage caused by NaIO3 in mice. Male and female C57BL/6J mice were injected with NaIO3 at 11 mg/kg BW (a) and 10 mg/kg BW (b) via tail vein and analyzed 7 days later, as described in Figure 1. On the left, two representative images of RPE flat-mounts with ZO-1 immunofluorescence (green) are shown for male and female mice with each dose. On the right, the quantification results of all mice in each group are shown. The proportions (%) of the three regions, normal RPE (periphery), elongated RPE (transitional zone), and damaged RPE (center), were calculated compared to the entire RPE. The values represent the means (horizontal lines) and 95% confidence intervals (error bars). The values were compared between male and female mice, and statistical significance was determined by Student’s t test (unpaired, two-tailed), which is shown by ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001. The RPE was more susceptible to NaIO3 in female mice than in male mice. (c) RPE gene expression changes induced by NaIO3 in male and female mice. Male (labeled as M) and female (labeled as F) C57BL/6J mice were injected with NaIO3 at 11 mg/kg BW via tail vein, and expression of selected genes in the RPE was analyzed by RT-qPCR at 0, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h after NaIO3 injection. Relative expression at each time point was calculated as the ratio to the average of 4 females and 4 males at 0 h and presented as log2. Expression changes of some genes were more profound and/or prolonged in female mice than in male mice. (d) Correlation of the expression of selected genes in individual samples. Based on the similar patterns of expression changes revealed in (c), correlation of relative expression of Cat and Sirt5 to that of Rlbp1 and two RPE transcription factors Otx2 and Mitf in individual samples was analyzed by linear regression. A strong correlation was observed in the expression levels between Cat and Rlbp1 and between Cat and Otx2 or Mitf.
