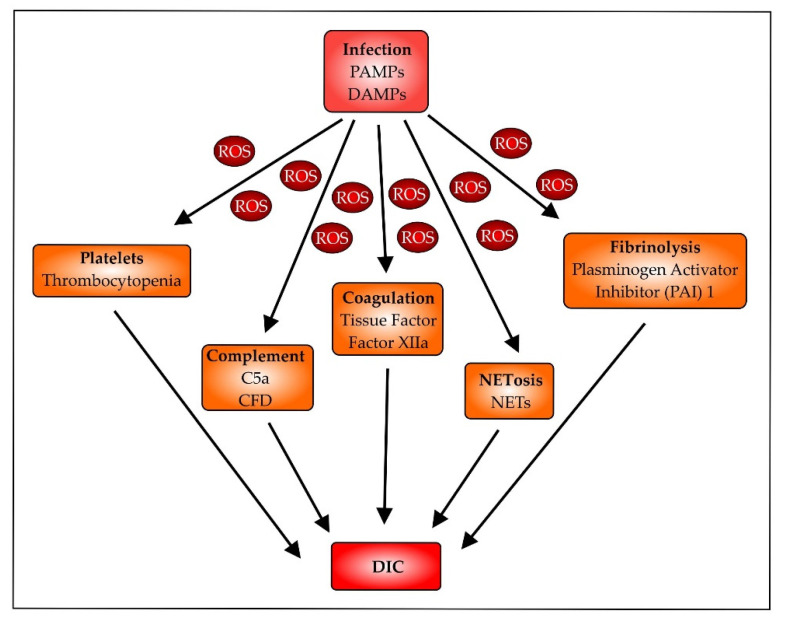
Figure 5.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Infectious pathogens via their associated PAMPs release resultant DAMPs, following cell activation or damage, leading to ROS production. These proinflammatory mediators contribute to the activation of platelets, leading to thrombocytopenia [175]; attract immune cells due to the liberation of the chemotactic complement factor C5a [89]; induce tissue factor (TF) production by endothelial cells [169]; and increase coagulation factor FXIIa [166] and plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI) I, reducing fibrinolysis [173].