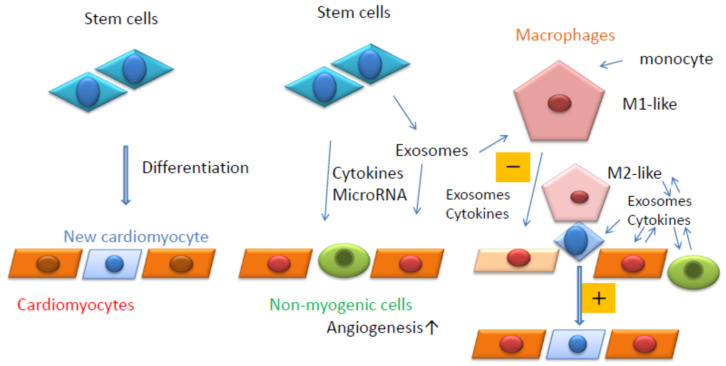
Figure 2.
Summary of the current review. Stem cells can differentiate into cardiomyocytes (Left). Stem cells can release cytokines, microRNAs, and exosomes. Exosomes also contain cytokines and microRNAs (Middle). Resident macrophages can contact stem cells in close proximity to cardiomyocytes and induce their differentiation into cardiomyocytes (Right). Resident macrophages and monocyte-derived macrophages are affected by exosomes secreted by surrounding cells and can affect the surrounding cells positively (M2-like, +) or negatively (M1-like, −) (Right).