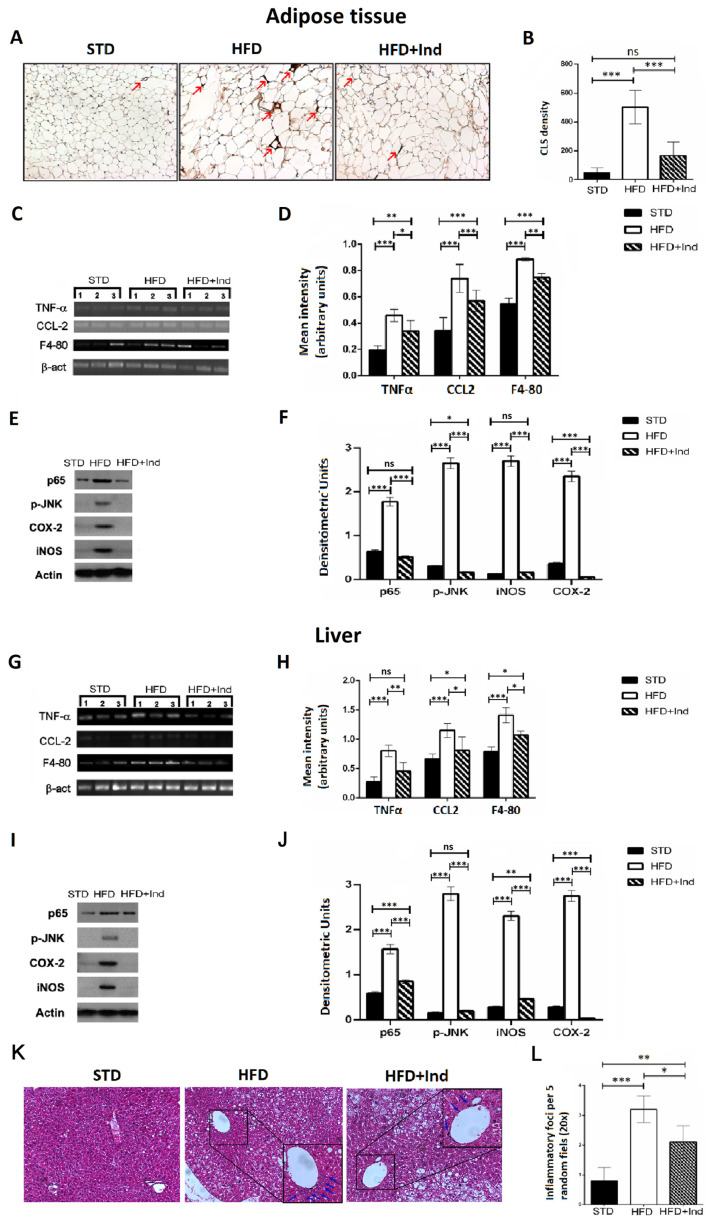
Figure 6.
Indicaxanthin treatment prevents inflammation in visceral adipose tissue and liver of HFD-fed mice. Immunohistochemistry analysis in epididymal visceral adipose tissue (VAT) for MAC-2 positive macrophages forming CLS (arrows) (magnification 10×) (A); density of MAC-2 positive CLS in VAT (B); mRNA expression of TNF-α, F4-80, and CCL-2 and β-actin by PCR in VAT (C) and liver (G); densitometric analysis of PCR results in VAT (D) and liver (H); representative Western blot bands of adipose tissue (E) and hepatic (I) p65, pJNK, iNOS, COX-2 and β-actin protein expression; densitometric analysis of adipose tissue (F) and hepatic (J) p65, pJNK, iNOS and COX-2 protein levels normalised for β-actin levels; liver histology of examined by H&E staining (K). Arrows indicate the points of inflammatory foci (magnification 10×). Quantification of inflammatory foci per 5 random fields under 20× magnification (L). Results are shown as means ± SEM of 8 animals/group. ns: p > 0.05; * p ≤ 0.05; ** p ≤ 0.01; *** p ≤ 0.001 (ANOVA associated with Bonferroni’s correction).