Figure 7.
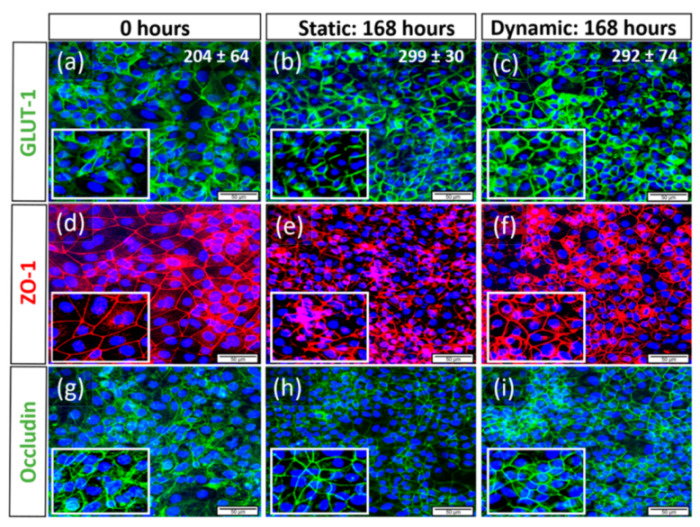
Changes of cell morphology and protein expression of hiPSC-derived BCECs compared between dynamic and static culture conditions, representative images of N = 3 biological replicates, scale bar = 50 µM, magnification = 40×. Via immunofluorescence, the expression of the Glucose transporter-1 (GLUT-1, (a–c)), as well as the TJ proteins Zonula Occludens-1 (ZO-1, (d–f)) and Occludin (g–i), was observed. In both 168 h static and dynamic conditions, BCECs showed more nuclear compaction and increased expression of relevant proteins such as GLUT-1 (b,c), ZO-1 (e,f), and Occludin (h,i), respectively, when compared to 0 h static conditions (a,d,g). Zoomed in frames show more cytoplasmic localization of GLUT-1 (a) at day 0 when compared to 168 h dynamic conditions (c). In all markers, we observed more pronounced protein localization at the cellular borders post-168 h of static (zoomed in frame (b,e,h)) and dynamic conditions (c,f,i). However, BCECs cultivated under 168 h of flow showed more continuous and smooth membranous staining patterns, while BCECs of long-term static culture represented discontinuous staining patterns. The cell numbers counted for each culture condition are inserted in the upper right corner of the respective images (a–c).
