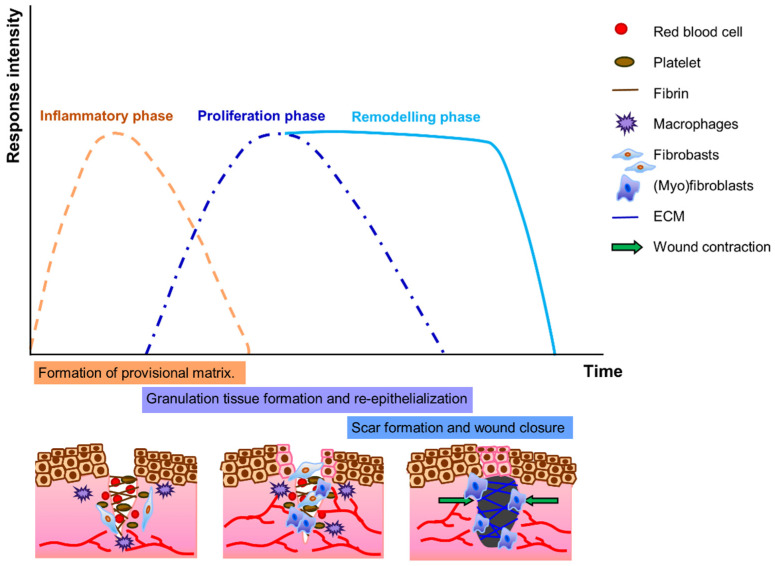
Figure 2.
Wound healing phases. In the inflammatory phase, fibroblasts synthesize a provisional matrix consisting of fibrin. Platelets release multiple chemokines that recruit inflammatory cells, including macrophages, as well as fibroblasts. In the proliferation phase, a new capillary network develops and contributes to the proliferation of fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are transient to (myo)fibroblasts, which encourages the synthesis of ECM for maturation of granulation tissue. During the remodeling phase, scar tissue is formed by ECM remodeling, replacement of collagen III by collagen I, and an increase in elastin in the tissue. (Myo)fibroblasts contract the scar tissue and the wound is closed.