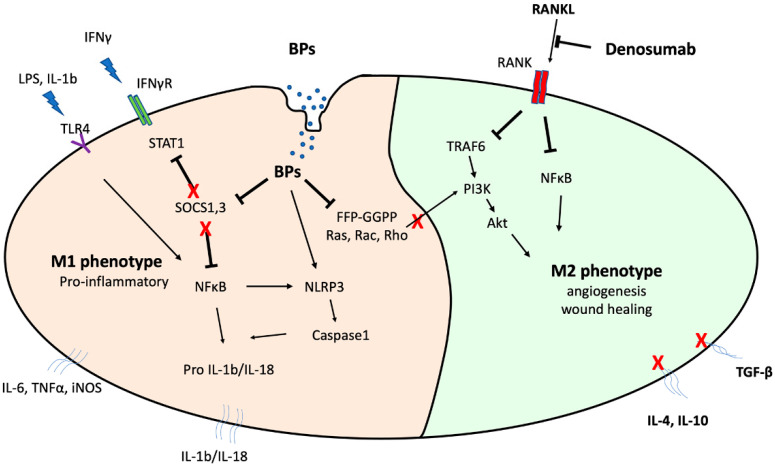
Figure 1.
In vitro effects of antiresorptives on macrophage signaling cascades. BPs’ internalization by macrophages results in inhibition of the mevalonate pathway and SOCS1/3 signaling and augments NLRP3 inflammasome activity. Moreover, BPs enhance IFNγ/STAT1 and TLR4 signaling, driving to NFκB hyper-activity. In addition, downregulation of key mevalonate enzymes inhibits PI3K-dependent M2 polarization. Altogether, BPs favor M1 polarization and contribute to a pro-inflammatory phenotype that results in mature IL1b/IL18 synthesis as well as IL6, iNOS, and TNFα release. Denosumab administration inhibits RANK downstream signaling pathways, including NFκΒ- and PI3K/AKT-dependent M2 polarization. (NLRP3, NOD-like receptor proteins 3; SOCS, Suppressors of cytokine signaling; STAT, Signal transducer and activator of transcription; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3 kinases).