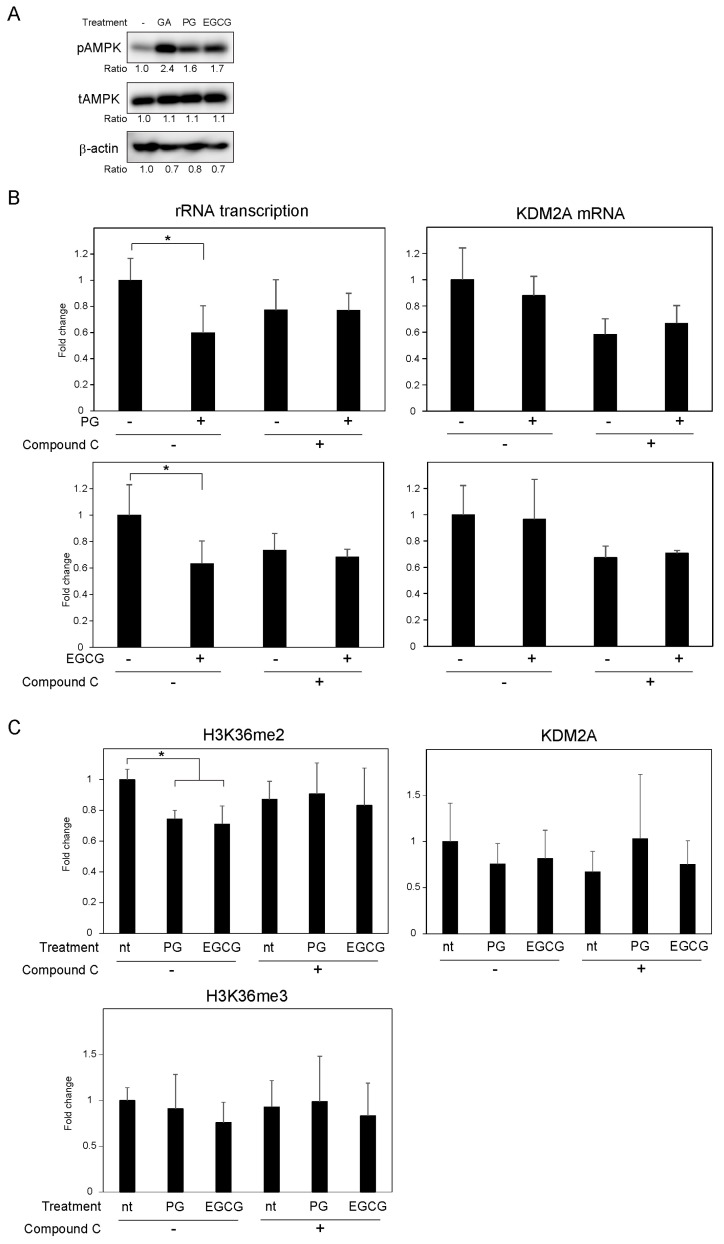
Figure 2.
PG- and EGCG-mediated activation of AMPK is required for the decrease in the levels of histone H3K36me2 in the rRNA gene promoter and consequent rRNA transcription. (A) MCF-7 cells were treated with 50 μM GA, PG, or EGCG for 4 h. The cells were then lysed, and the levels of phosphorylated-AMPKα (Thr172) (pAMPK), total AMPKα (tAMPK), and β-actin were analyzed via immunoblotting. (B) MCF-7 cells were treated with (+) or without (-) 50 μM PG or EGCG in the presence (+) or absence (-) of 10 μM compound C, an AMPK inhibitor, for 4 h. Total RNA was extracted, and the levels of rRNA transcripts (pre-rRNA) (left panel) and KDM2A mRNA (right panel) were determined using qRT-PCR. The results are shown as the fold change in relation to cells in the absence of compounds. (C) MCF-7 cells were treated with or without 50 μM PG or EGCG in the presence (+) or absence (-) of 10 μM compound C for 4 h. The levels of H3K36me2, H3K36me3, and KDM2A in the rRNA gene promoter were analyzed by ChIP assay. The results are shown as the fold change in relation to cells in the absence of compounds. The experiments in (B,C) were performed more than three times, and the mean values with standard deviations are shown. * p < 0.05.