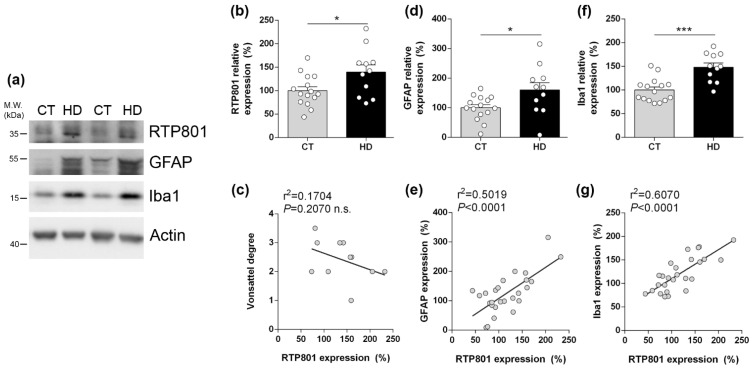
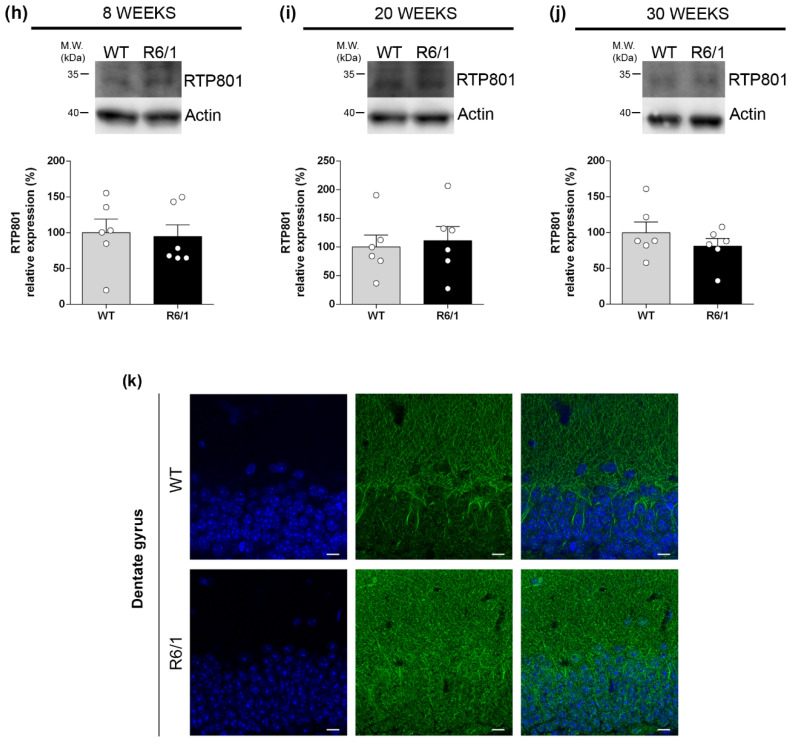
Figure 1.
RTP801 levels are increased in the hippocampus of HD patients and correlate with neuroinflammatory markers but are not altered in the R6/1 mouse. (a) Immunoblotting for RTP801, GFAP, Iba1, and actin as loading control in total homogenates from human post-mortem hippocampal samples from non-affected individuals (CT) and Huntington’s disease (HD) patients. Densitometric quantifications of RTP801 (b), astrogliosis marker GFAP (d), and microgliosis marker Iba1 (f). Pearson’s correlation analysis comparing RTP801 levels as in (b) with Vonsattel grades (c), GFAP levels (e), and with Iba1 levels (g) per sample. (h–j) Immunoblotting for RTP801 and actin as loading control in total homogenates from 8, 20, and 30 weeks old wild-type (WT) and R6/1 mice. (i) Densitometric quantification of RTP801 protein levels. Data in (b,d,f,i) is represented as mean ± SEM and was analyzed with Student’s t-test. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001 vs. CT. (k) RTP801 immunostaining in 8-week-old WT and R6/1 mouse hippocampus (dentate gyrus). Coronal sections were stained with an antibody against RTP801 (in green) and nuclei were visualized with Hoechst 33352 staining (in blue). Scale bars, 10 µm.