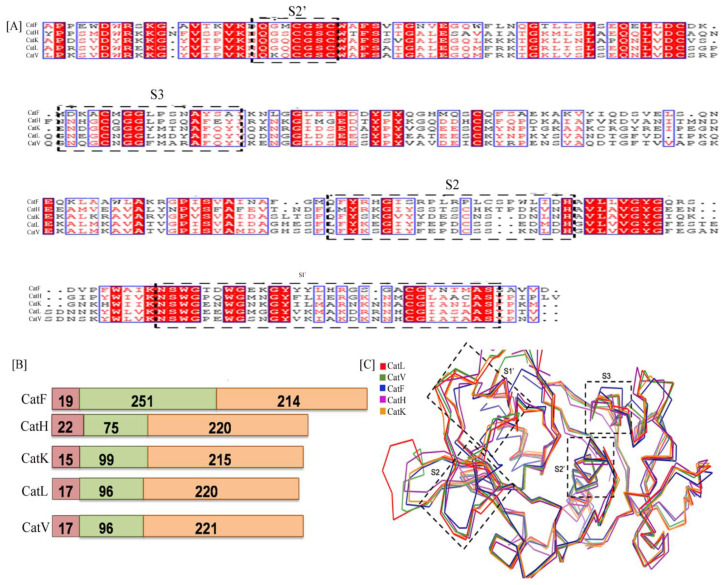
Figure 2.
(A) The multiple sequence alignment representation of different cathepsins namely CatL (PDB Id. 4AXL), CatK (PDB Id. 6ASH),CatV (PBD Id. 1FH0),CatH (PDB Id. 1NB3), CatF (PDB Id. 1M6D): figure generated by Clustal Omega and Espript3. The substrate binding subsites S2′, S3 of L-domain and S2, S1′of R-domain are highlighted with dotted box. The figure [highlighted in red] denotes sequence conservation of active site residues at their respective subsites. (B) The domain architecture of cathepsin indicates conservation in overall functional classification of domains SD represents the signal sequence domain, PD as prodomain, MD is the mature domain; Number of amino acid present in each domain is mentioned. (C) Superposition of backbone traces of five cathepsins indicate sequence diversity in domains S1, S2, S3 and S1′ has generated three dimensional perturbations.