Figure 9.
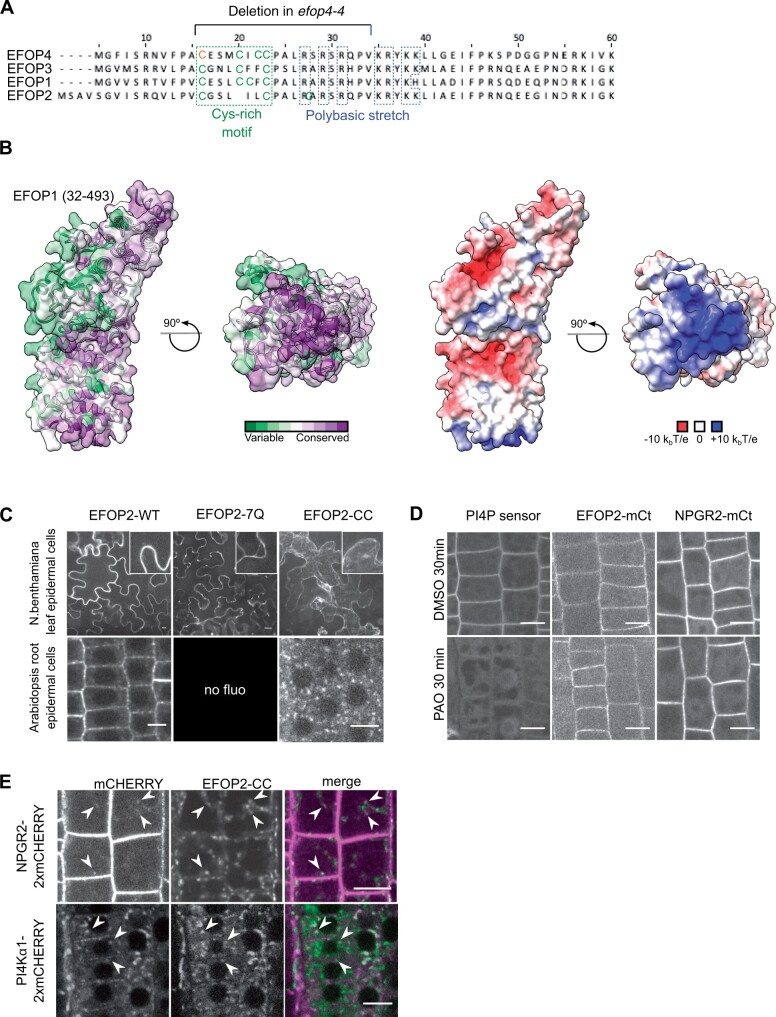
The EFOP subunit determines PI4Kα1 localization by lipid anchoring. A, N-terminal sequence alignment of EFOPs proteins. Conserved cys-rich motif (green) and polybasic patch (blue) are indicated, as well as, the deletion in efop4-4 CrisPr allele. Bold cysteines are predicted as S-acetylated on the SwissPalm database with high (green) and medium (orange) confidence level. B, Template-based model of the EFOP1 structure (amino acid range 32–493). The left side shows an analysis of conserved amino acid residues mapped on the solvent-excluded surface of EFOP1. The right side shows electrostatic potential mapped on the solvent-excluded surface of EFOP1. The figure shows that the N-terminally located basic patch is highly conserved. C, Confocal images of EFOP2–mCITRINE (wild-type), EFOP2-7Q–mCITRINE, and EFOP2-CC–mCITRINE in N. benthamiana leaf epidermal cells and Arabidopsis root epidermal cells. Scale bar: 10 μm. D, Confocal images of PI4P sensor (PH domain of FAPP1 carrying the mutation E50A), EFOP2–mCITRINE (EFOP2-mCt), and NPGR2–mCITRINE (NPGR2–mCt) treated for 30 min with 30 μM PAO or the equivalent volume of DMSO. Scale bar: 10 μm. E, Confocal images of Arabidopsis root epidermal cells co-expressing EFOP2-CC-mCITRINE and NPGR2-2xmCHERRY or PI4Kα1-2xmCHERRY. White arrows indicate internal structures where the two signals colocalize. Scale bar: 10 μm.