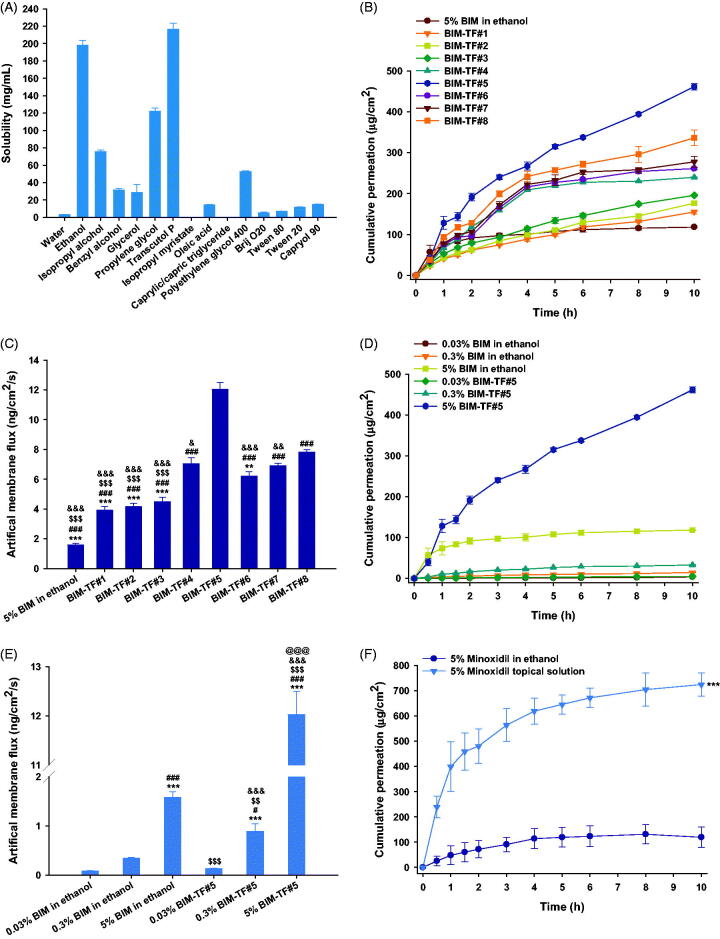
Figure 1.
(A) Solubility of bimatoprost (BIM) in various solvents and surfactants. In vitro penetration of BIM topical formulations (BIM–TFs) through the artificial membrane; (B) time–course curve showing cumulative drug infiltration and (C) flux from BIM in ethanol or BIM–TFs. **p<.01, ***p<.001 compared to BIM–TF#4; ###p<.001 compared to BIM–TF#5; $$$p<.001 compared to BIM–TF#7; &p<.05, &&p<.01, &&&p<.001 compared to BIM–TF#8. (D) Time–course curve showing cumulative infiltration and (E) flux of 0.03%, 0.3%, and 5% BIM in ethanol or BIM–TF#5. ***p<.001 compared to 0.03% BIM in ethanol; #p<.05, ###p<.001 compared to 0.3% BIM in ethanol; $$p<.01, $$$p<.001 compared to 5% BIM in ethanol; &&&p<.001 compared to 0.03% BIM–TF#5; @@@p<.001 compared to 0.3% BIM–TF#5. (F) Time–course curve showing cumulative drug penetration of 5% minoxidil in ethanol and commercial 5% minoxidil topical solution through an artificial membrane. ***p<.001 compared to 5% minoxidil in ethanol. Values are means ± SDs (n = 4 for each group).