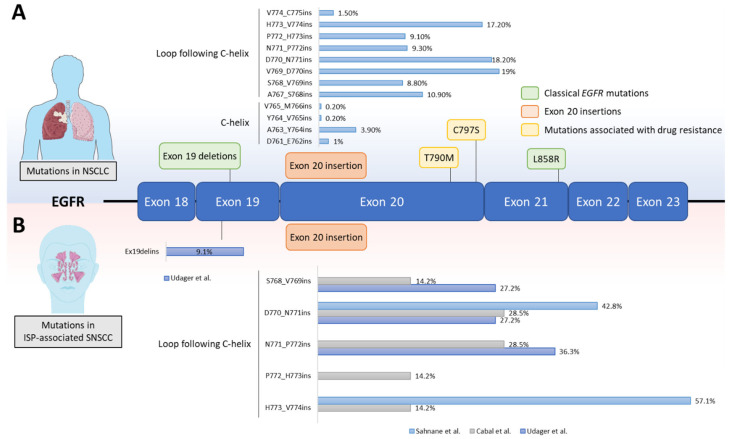
Figure 2.
EGFR mutations in NSCLC and ISP-associated SNSCC. A schematic representation of the EGFR kinase domain is shown. (A) All EGFR mutations in NSCLC are clustered across exon 18–22, which encode the tyrosine kinase domain. The most common EGFR mutations in NSCLC are referred to as ‘classical’ EGFR mutations (green) and account for approximately 85% of all EGFR mutations in NSCLC patients. The point mutations T790M and C797S (yellow) are associated with resistance to first- and third-generation EGFR TKIs, respectively. The prevalence of exon 20 insertions (orange) in NSCLC that occur at different amino acid positions are shown in the bar chart. Mutation frequency distribution was calculated using COSMIC v86 (http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk, 10 November 2021) after filtering for NSCLC adenocarcinoma patients with exon 20 insertions (n = 383) [55]. (B) Frequency of exon 20 insertions and exon 19 deletion-insertion in ISP-associated SNSCC across 3 different studies are shown in the bar charts [19,20,56].