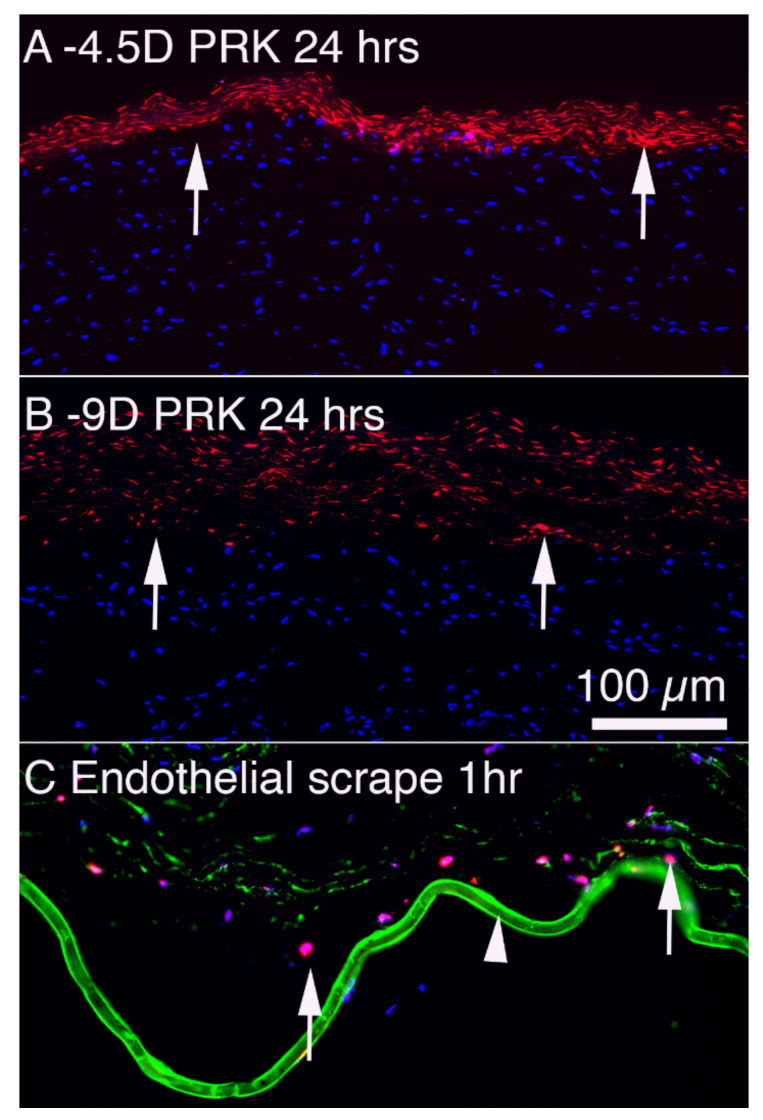
Figure 4.
Keratocyte apoptosis in response to injury in rabbit corneas. (A) TUNEL assay at 24 h after −4.5D PRK that entails epithelial debridement and then anterior stromal ablation with the excimer laser. Arrows indicate anterior stromal keratocytes undergoing apoptosis. The apoptotic cells can be detected with TEM within moments of epithelial scrape but become strongly TUNEL+ from 4 to more than 24 h. Many bone marrow-derived cells such as monocytes and fibrocytes detected with markers such as CD34, CD45, and CD11b infiltrate the stroma from the limbus and many also undergo apoptosis in the first 24 to 72 h. (B) At 24 h after −9D PRK, with twice the number of excimer laser pulses, many more anterior stromal keratocytes (arrows) undergo apoptosis. Thus, there is a correlation between the magnitude of the anterior corneal injury and the number of keratocytes that undergo early apoptosis [19]. (C) At 1 h following an 8 mm corneal endothelial scrape injury, many posterior stromal keratocytes (arrows) undergo apoptosis detected with the TUNEL assay. Note the edema of the stroma that also occurs immediately after endothelial injury. The arrowhead indicates DBM stained (green) for BM component nidogen-1. Figures (A,B) were previously unpublished but from the study of Mohan et al., 2003 [19]. Figure (C) reprinted with permission from Medeiros et al. Exp. Eye Res. 2018; 172:30-35.