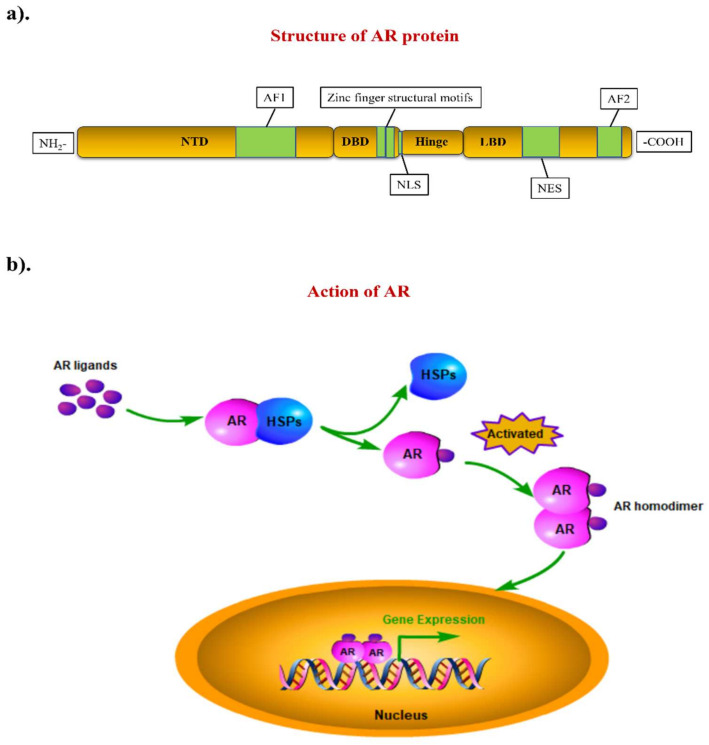
Figure 1.
The structure of AR and its molecular mechanism of action. (a) The AR gene is located on the X chromosome, it encodes a protein with four main components: the N-terminal transactivation domain (NTD), the DNA-binding domain (DBD), the hinge region and the ligand-binding domain (LBD). (b) Unactivated AR is located in the cytoplasm and binds to heat shock proteins (HSPs). When stimulated by androgen, AR separates from HSPs rapidly, followed by forming homodimers and translocating into the nucleus to regulate the expression of its target genes.