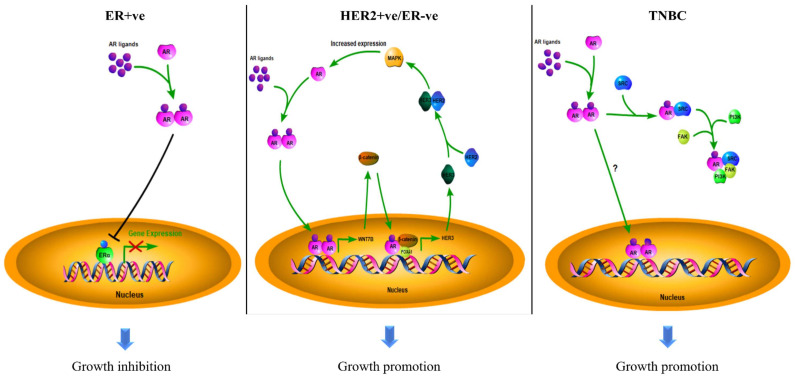
Figure 2.
The roles of AR in different sub-types of breast cancer. The mechanisms of action of AR in breast cancers depend on the disease sub-type: AR suppresses ERα in ER + ve cancers to inhibit tumor growth; AR promotes HER2 + ve/ER-ve cell growth by interacting with WNT/β-catenin to induce the expression of HER3, further binding to HER2 to activate the MAPK pathway, which in turn enhances the activity of AR; AR drives TNBC development and progression by activating the SRC/PI3K/FAK pathway. However, the DNA targets of AR are not well characterized in TNBC.