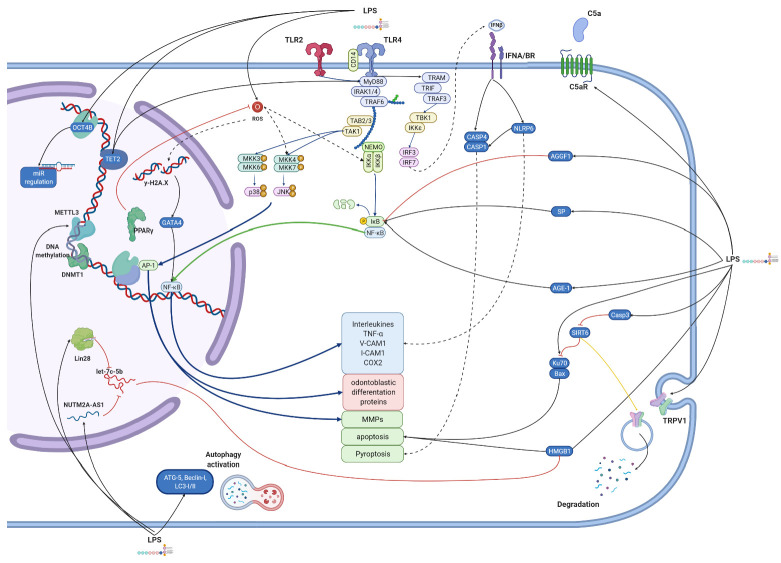
Figure 3.
Molecular effects exerted by lipopolysaccharides on human dental pulp cells (hDPCs). Figure summarizes results from studies conducted on hDPCs, regardless of LPS origin. The main pathway activated by LPS involves TLR2/4 receptor. Groups of proteins transducing signal are colored differently. TLR pathway, via NF-κB and MAPK, promotes release of interleukins (mainly IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8), adhesive molecules (I-CAM, V-CAM), metalloproteases (MMPs) and odontoblastic differentiation proteins. This pathway is marked with thick blue arrows. LPS increases ROS activity in cells, changes microRNA profile, leads to apoptosis or pyroptosis. A variety of different pathways and particles activated in LPS-treated cells are presented both in deep blue brackets and by protein images with their names. Black arrows represent positive stimulation, dashed arrows show indirect activation, red ones—inhibition, yellow—ubiquitination, green—translocation to another cell compartment. Created with BioRender.com 7 December 2020.