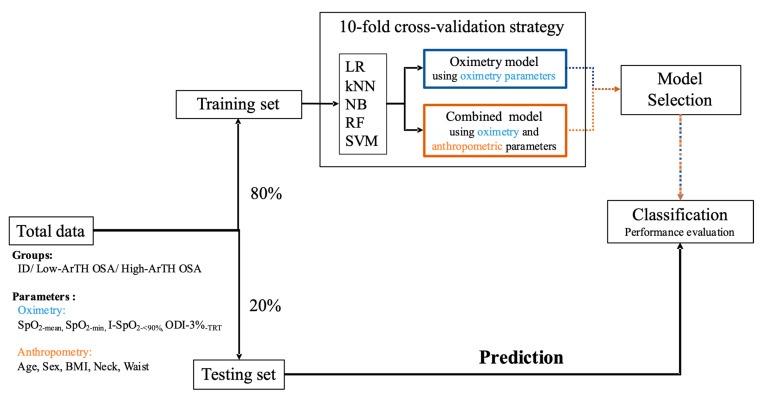
Figure 3.
Model establishment process. All data were separated at a ratio of 80:20 to act as the training–validation dataset and testing dataset. The k-fold cross-validation technique (k = 10) was employed in the training–validation stage to separately develop two types of models through five machine learning approaches. Subsequently, the models with the highest accuracy in oximetry typing and combined parameter typing were respectively used to predict the testing dataset for evaluating the overall accuracy and input feature importance. Abbreviations: ID: insomnia disorder; ArTH: respiratory arousal threshold; OSA: obstructive sleep apnea; LR: logistic regression; kNN: k-nearest neighbors; NB: naive Bayes; RF: random forest; SVM: support vector machine; SpO2-mean: mean level of peripheral arterial oxygen saturation measured using pulse oximetry; SpO2-min: minimum level of peripheral arterial oxygen saturation measured using pulse oximetry; I-SpO2-<90%: index for the ratio of the amount of time during which the peripheral arterial oxygen saturation measured using pulse oximetry is lower than 90% to the sleep period time; ODI-3%-TRT: total number of oxygen desaturation events (>3%) divided by the total recording time; BMI: body mass index.