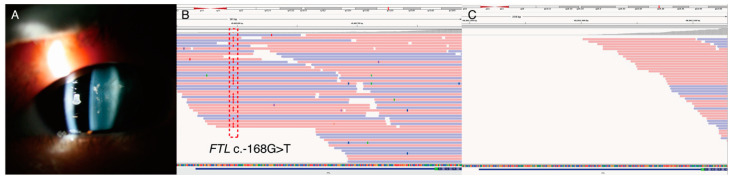
Figure 4.
(P38) A 7-year-old male had congenital cataracts in both eyes. Laboratory examination showed elevated ferritin level 1205.3 ng/mL (reference range: 23.9~336.2 ng/mL) without iron overload. The inheritance pattern was consistent with autosomal dominant. (A) Slit-lamp examination showed congenital cataracts since early childhood. (B) Integrative genomic viewer showed FTL c.-168G>T variant in upstream to starting codon. This region was included in our panel, and the variant was previously reported as pathogenic. (C) The 5′ untranslated region of exon 1 in FTL gene was not covered in commercially available exome sequencing. Molecular diagnosis of hyperferritinemia-cataract syndrome enables us to avoid unnecessary investigations or treatment such as repeated phlebotomy or liver biopsy.