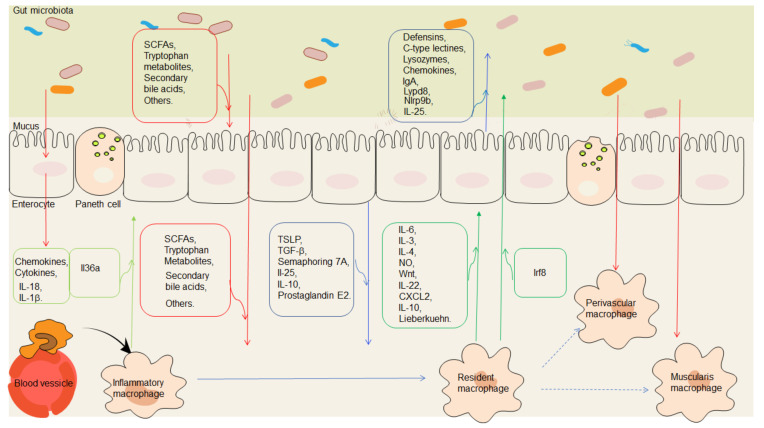
Figure 1.
A special network comprised of macrophages, the gut microbiota, and epithelial cells for gut homeostasis. Immunological mediators, including cytokines and chemokines secreted from the gut epithelial cells stimulated by gut microbiota, such as IL-18 and IL-1β, modulate host immune responses and maintain a well-balanced relationship between gut microbes and the host immune system. The metabolites of the gut microbiota, such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), tryptophan metabolites, secondary bile acids, and polyamines, regulate the proliferation and function of the gut epithelial cells. The metabolites of the gut microbiota, such as SCFAs, tryptophan metabolites, secondary bile acids, UroA/UAS03, polysaccharide, and polyamine can promote the differentiation of macrophages into resident macrophages. Substances such as defensins, c-type lectins, lysozymes, chemokines, Ly6/Plaur domain-containing 8 (Lypd8), Nlrp9b, and interleukin (IL)-25, produced by the gut epithelial cells, especially Paneth cells, also have effects on the gut microbiota. Intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) also produce factors such as thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), TGFβ, semaphoring 7A, transforming growth factor (TGF-β), retinoic acid, IL-25, and apoptotic cells to promote the macrophages into resident macrophages. Conversely, macrophages can generate some factors such as IL-6, IL-3, IL-4, nitric oxide (NO), Wnt, IL-10, and Lieberkuehn to regulate the proliferation and function of the gut epithelial cells. Meanwhile, macrophages can directly or indirectly produce effects on the gut microbiota. Recent studies have also found effects of the gut microbiota on the perivascular macrophages and muscularis macrophages. Red lines with arrows indicate that the effects of the gut microbiota or their metabolites in the gut contents on the macrophages or gut epithelial cells. Blue lines with arrows indicate that effects of the gut epithelial cell derived factors on the macrophages or gut microbiota. Green lines with arrows indicate the effects of the macrophage derived factors on the gut epithelial cells or gut microbiota. Boxes indicate the components from the gut microbiota, gut epithelial cells, or macrophages.