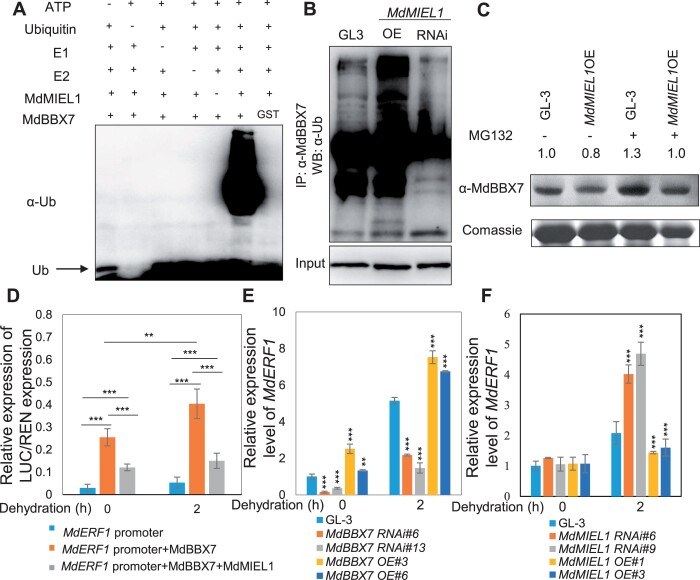
Figure 6.
MdMIEL1 ubiquitinates and degrades MdBBX7, and inhibits its transcriptional activity. A, MdMIEL1 ubiquitinated MdBBX7 in vitro. The ubiquitination status of MdBBX7 was detected in the presence of ubiquitin E1, E2, and MdMIEL1 using an anti-ubiquitin antibody. B, MdMIEL1 ubiquitinated MdBBX7 in vivo. Total protein was extracted from GL-3, MdBBX7 OE, and MdBBX7 RNAi transgenic plants and immunoprecipitated with anti-MdBBX7 antibody, and was subjected to western blot analysis with anti-ubiquitin. WB, western blot. C, The MdBBX7 protein was degraded by MdMIEL1 via the 26S proteasome pathway. Four-week-old tissue-cultured GL-3 and MdMIEL1 OE transgenic plants were treated with or without the proteasome inhibitor MG132 for 12 h. The proteins were extracted from GL-3, MdMIEL1 OE transgenic plants and immunoblotted with anti-MdBBX7 antibody. D, Relative luciferase activity from the dual luciferase reporter assays in N. benthamiana leaves. Pro35S::REN was used as an internal control. Quantification was performed by normalizing firefly luciferase activity to that of renilla luciferase. E, Expression of MdERF1 in MdBBX7 RNAi and OE plants in response to drought stress. F, Expression of MdERF1 in MdMIEL1 RNAi and OE plants in response to drought stress. Data are means ± sd (n = 5 in (D), 3 in (E) and (F)). Asterisks indicated values significantly different between the transgenic lines and the GL-3 in each group (0 h and 2 h) or the line indicated. One-way ANOVA (Tukey’s test) was performed, and statistically significant differences are indicated by **P < 0.01, or ***P < 0.001.