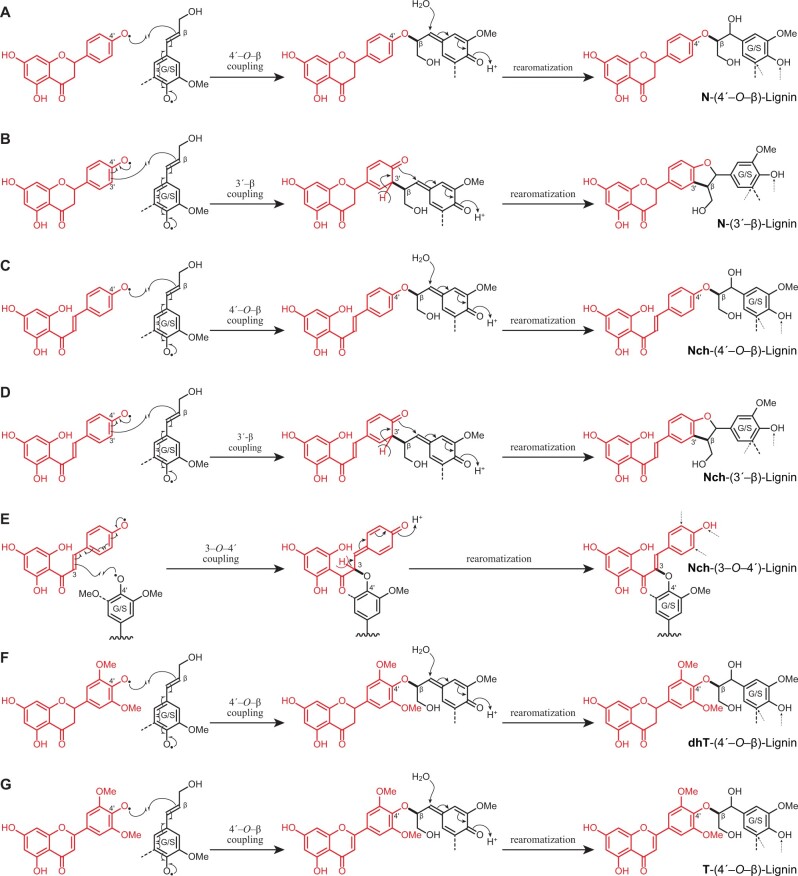
Figure 7.
Dehydrodimerization products arising from oxidative cross-coupling of the different flavonoids (naringenin, naringenin chalcone, dihydrotricin, and tricin) with monolignols. A, 4′–O–β Coupling of naringenin and a monolignol producing aryl alkyl ethers; B, 3′–β Coupling of naringenin and a monolignol producing phenylcoumaran structures; C, 4′–O–β Coupling of naringenin chalcone and a monolignol producing aryl-alkyl ethers; D, 3′–β Coupling of naringenin chalcone and a monolignol producing phenylcoumaran structures; E, 3–O–4′ Coupling of naringenin chalcone and the growing lignin chain producing alkyl-aryl ethers and conserving the double bond; F, 4′O–β Coupling of dihydrotricin and a monolignol producing aryl-alkyl ethers; G, 4′–O–β Coupling of tricin and a monolignol producing aryl-alkyl ethers. Sites of possible further radical coupling on the products are shown via small dashed arrows; obviously coupling can only occur if the site is unoccupied, when the dashed bond is an H and not, for example, an OMe in a syringyl unit.