Figure 5:
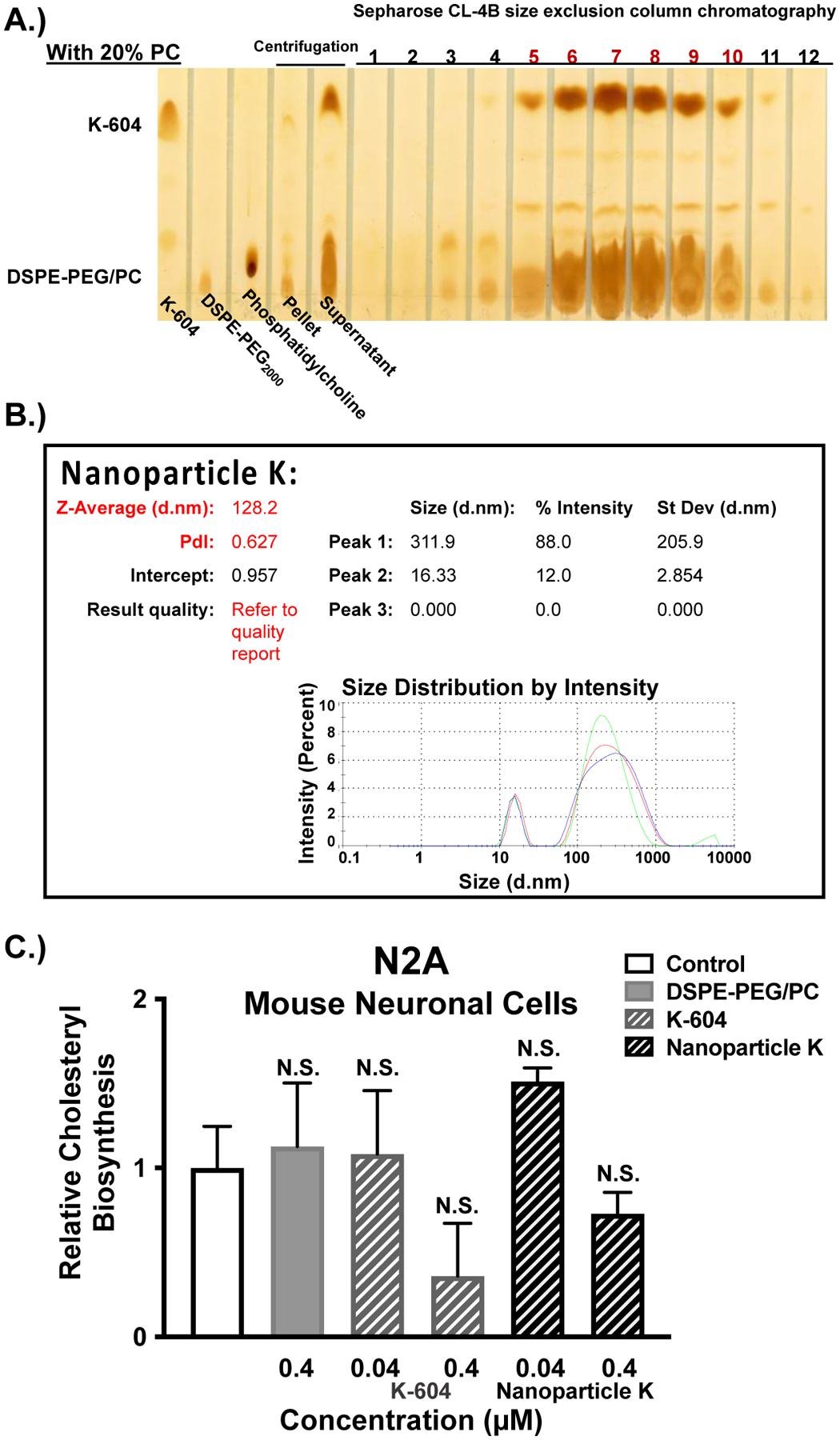
ACAT inhibitor, K-604, is encapsulated at high concentration by using the nanoparticle protocol and displays similar characteristics to Nanoparticle F. A.) Standards (K-604, DSPE-PEG2000, and phosphatidylcholine) are shown in the first 3 lanes followed by the pellet and supernatant samples. The fractions labeled 1–12 refer to the 12 elution fractions, each with 500μL, collected from a size exclusion column (Sepharose CL-4B). The red numbers highlight the elution fractions containing encapsulated nanoparticles of K-604 (Nanoparticle K), based on the co-elution of K-604 with DSPE-PEG2000/PC. The overall Nanoparticle K formulation is 40 mol % K-604 (12mM), 20 mol % PC (6mM), and DSPE-PEG2000 (30mM). B.) Malvern Zeta Sizer “Size Distribution by Intensity” result for freshly solubilized Nanoparticle K. Each sample was measured in triplicate C.) Mouse neuronal (N2a) cells at 80–90% confluency in triplicate (12-well dishes) were either treated for 2 hours with EtOH (control) or with the following agents: 0.4μM DSPE-PEG2000/PC; 0.04μM or 0.4μM of K-604 alone or Nanoparticle K. The cells were then pulsed with 3H-oleate to determine ACAT activity as described in the Methods and Materials section. One-way ANOVA statistical test was completed, and results shown are relative to the control (0.4μM K-604 p-value = 0.08; 0.4μM Nanoparticle K p-value = 0.8). N.S. not significant.
