FIGURE 2.
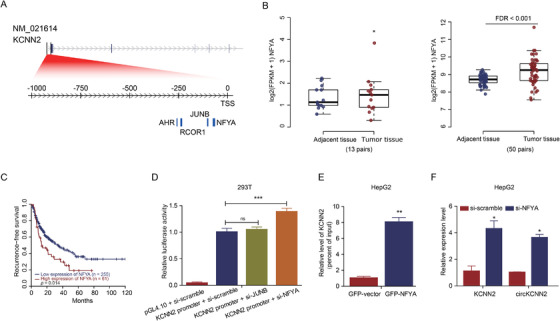
The identification of the functional transcription factor regulating KCNN2 and circKCNN2. (A) The putative transcription factors (posterior probabilities > 0.8) and their binding sites. NFYA: ‐64 bp to ‐76 bp; JUNB: ‐98 bp to ‐105 bp; RCOR1: ‐232 bp to 241 bp; AHR: ‐256 bp to ‐261 bp. (B) The expression levels of NFYA in the tumor and adjacent tissues. Left: in the training cohort of this study. Right: in the TCGA LIHC cohort. (C) The association between the intratumor level of NFYA and the recurrence‐free survival of HCC patients from LIHC cohort. (D) Results of luciferase assays. pGL4.10, empty vector of luciferase reporter; KCNN2 promoter, the luciferase reporter containing the sequence of KCNN2 promoter; si‐scramble/si‐JUNB/si‐NFYA, siRNA targeting scramble sequence/JUNB/NFYA. The group of KCNN2 promoter + si‐scramble served as a reference to calculate a relative value of luciferase activity. (E) Results of ChIP followed qPCR testing the enrichment level of KCNN2 promoter in the DNA pulled down by GFP‐Trap Agarose. GFP‐NFYA/‐vector, DNA from cells transfected with the overexpression plasmid of GFP tagged NFYA/the control vector. The group of GFP‐vector served as a reference to calculate a relative enrichment. (F) RT‐qPCR results displaying the levels of KCNN2 and circKCNN2. The groups of si‐scramble served as references to calculate relative RNA levels. Cellular experiments were performed in triplicate. N = 3 for each group. ns, no statistically significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
