FIGURE 3.
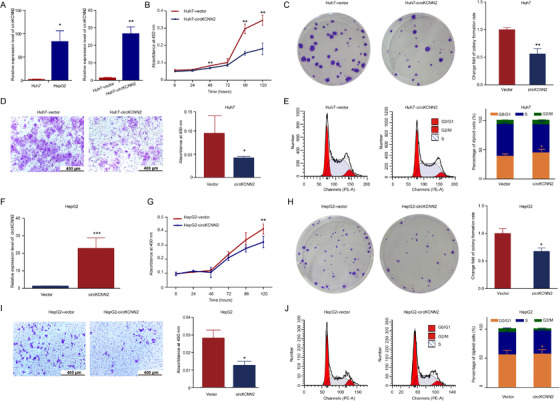
The effect of ectopic overexpression of circKCNN2 on the proliferation, colony formation, and migration of Huh7 and HepG2 cells. (A) RT‐qPCR results of circKCNN2 expression. Left, the inherent level of circKCNN2 in Huh7 and HepG2 cells. Huh7 cells served as a reference to calculate relative expression levels. Right, ectopic overexpression of circKCNN2 in Huh7 cells. Huh7‐vector (reference for normalization), cells infected with control lentivirus; Huh7‐circKCNN2, cells infected with circKCNN2 overexpression lentivirus. (B) CCK8 assays showed that ectopic overexpression of circKCNN2 inhibited the proliferation of Huh7 cells. (C) The colony formation was inhibited in Huh7‐circKCNN2 cells. (D) Transwell assays showed that ectopic overexpression of circKCNN2 inhibited the migration of Huh7 cells. (E) The rate of cells in G0/G1 was significantly higher in Huh7‐circKCNN2 cells than that in Huh7‐vector cells. (F) The expression level of circKCNN2 in HepG2 cells. HepG2‐vector, cells infected with control lentivirus; HepG2‐circKCNN2, cells infected with circKCNN2 overexpression lentivirus. (G) Ectopic overexpression of circKCNN2 inhibited the proliferation of HepG2 cells. (H) The colony formation was inhibited in HepG2‐circKCNN2 cells. (I) Ectopic overexpression of circKCNN2 inhibited the migration of HepG2 cells. (J) The rate of cells in G0/G1 was significantly higher in HepG2‐circKCNN2 cells than that in HepG2‐vector cells. All the assays were performed at least three times. N = 3 for each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
