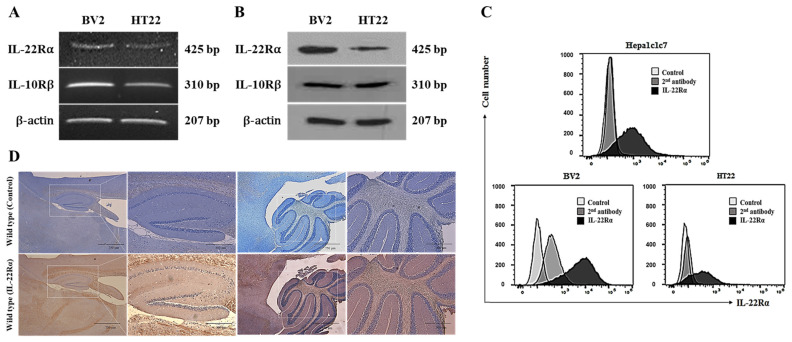
Figure 1.
IL-22Rα is constitutively expressed in BV2 and HT22 cells and mouse brain tissue. (A) RT-PCR analyses of IL-22Rα and IL-10Rβ in BV2 and HT22 cells. Total RNA was extracted from cells (1 × 106), and RT-PCR was performed using specific primers for IL-22Rα and IL-10Rβ, as described in the Materials and Methods. (B) Western blot analyses of IL-22Rα and IL-10Rβ in BV2 and HT22 cells. Protein was extracted from 1 × 106 cells and analyzed with -IL-22Rα Ab and anti-IL-10Rβ Ab, as described in the Materials and Methods. β-actin was used as a loading control. (C) Flow cytometry analyses of IL-22Rα in BV2, HT22, and Hepa1c1c7 cells. For each sample, 1 × 105 cells were collected, processed as described in the Materials and Methods, and then stained with an anti-mouse IL-22Rα antibody (2.5 µg/106 cells) as a primary antibody, and FITC-conjugated anti-rabbit Ab was used as a secondary antibody. IL-22Rα expression was analyzed as described in the Materials and Methods. (D) Immunohistochemical analysis of IL-22Rα expression in mouse brain. Paraffin-embedded tissues were sectioned with 4 μm thickness and incubated with a primary antibody against IL-22Rα and then with a biotinylated anti-rabbit antibody. ABC solution was loaded onto the sections for 30 min and a DAB kit was used for chromogenic detection. (A–D) Results are representative of three independent experiments.