Table 2.
Comparison of national, international, and patient specific prescribing and monitoring guidelines for trans women (observed males at birth) with gender dysphoria.
Hormone Dosing and Routine Long Term Monitoring (once stable/after 12-36 Months)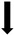
|
Maximum Oral Estradiol Dose (mg) | Maximum Transdermal Estradiol Dose (gel) (mg) | Maximum Transdermal Estradiol Dose (Patch)(mcg Twice Weekly) | ANNUAL MONITORING | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estradiol Level | Target Estradiol Level (nmol/L) | Testosterone | Liver Function Tests | Lipids | Glucose | HBA1c | Prolactin | Full Blood Count | FSH&LH | SHBG | Urea and Electrolytes | TSH | Vitamin D and Bone Profile | Blood Pressure | Weight | Breast Screening | Bone (DEXA) | AAA Screening | ||||
Guideline or Clinic
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| International | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| WPATH [10] | No specific dosing instructions given. WPATH recommends consulting Feldman and Safer [38] and Hembree et al. [39] for hormone regimes and lab monitoring protocols. Target estradiol levels “within a premenopausal female range but well below supraphysiologic levels”. Follow- up should also “include careful assessment for signs of cardiovascular impairment and venous thromboembolism through measurement of blood pressure, weight, and pulse; heart and lung exams; and examination of the extremities for peripheral edema, localized swelling, or pain” | Y | Y | |||||||||||||||||||
| Endocrine Society [11] A | 6 | 200 | Y | 360–735 B | Y | Y D | Y | Y E | ||||||||||||||
| National/Local | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Australia (children & adolescents) [40] | 4 | Y G | Y G | Y G | Y | Y | Y G | Y G | Y G | Y H | Y H | Y J | ||||||||||
| San Francisco [13] | 8 | 400 | Y K | physiological menstruating female range R | Y L | Y D | Y M | Y N | ||||||||||||||
| NHS Wales [28] | 8 | 4 | 200 | Y | 350–750 S | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | ||||||||
| NHS Scotland [27] | 6 | 3 | 200 | Y | 200–600 | Y | Y | “If risk factors” | Y | |||||||||||||
| GP CPD Red Whale [30] | 4 | 1.5 | 100 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N F | Y | ||||||
| GIC guidance | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| London Transgender clinic (private) | 8 | 3 | 200 | Y | 400–700 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N F | ||||||||
| Laurels NHS | 12 | 4 | 150 | Y | 200–600 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N F | ||||||||
| Gender GP (private) | 6 | 2 | 200 | Y | 300–800 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y P | |||||||||
| Sheffield NHS | 6 | 3 | 200 | Y | 300–600 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N F | Y | ||||||
| Tavistock NHS | 8 | 5 | 200 | Y | 400–600 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N F | Y Q | |||||||||
| Nottingham NHS | 8 | 6 | 400 | Y | 400–600 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y Q | Y Q | ||||||||||
| Gendercare (private) | 10 | 100 | Y | 400–600 R | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |||||||||||
| Leeds NHS | 8 | 6 | 400 | Y | 350–750 if aged < 40 yrs 300–600 if aged 40–50 yrs 200–400 if aged > 50 yrs or significant CV risk factors |
Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | |||||||||||
Key: Empty cell: no specific advice given; HBA1c, Glycated Haemoglobin; FSH&LH, Follicle Stimulating Hormone and Luteinizing hormone; SHBG, Sex hormone binding globulin; TSH, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone; A,”strong recommendations”; B, “level for premenopausal females (100 to 200 pg/mL)”; D, If on spironolactone; E, Consider screening at baseline. In individuals at low risk, screen at 60 years of age or if non compliant with hormone therapy; F, Unless prolonged periods without sex hormones or additional risk factors; G, Every 6 months; H, Every 3 months; J, Annually to document recovery after being on puberty suppression as required; K, Yearly or as required; L consider to “fine tune hormone regimes”; M, Dependent on age and length of exposure to estradiol; N, from age 65 years on (earlier if risk factors); P, advises if transwomen continue estradiol over 70 years of age they should “continue” receiving breast screening, although screening for younger transwomen is not specified; Q, screening as per https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/nhs-population-screening-information-for-transgender-people/nhs-population-screening-information-for-trans-people (accessed on 1 Jan 2022); R, consider stopping hormones at menopause age; S, older patients that wish to reduce their dose may do so, with a target level of 200-300 pmol/L; CV, cardiovascular.
