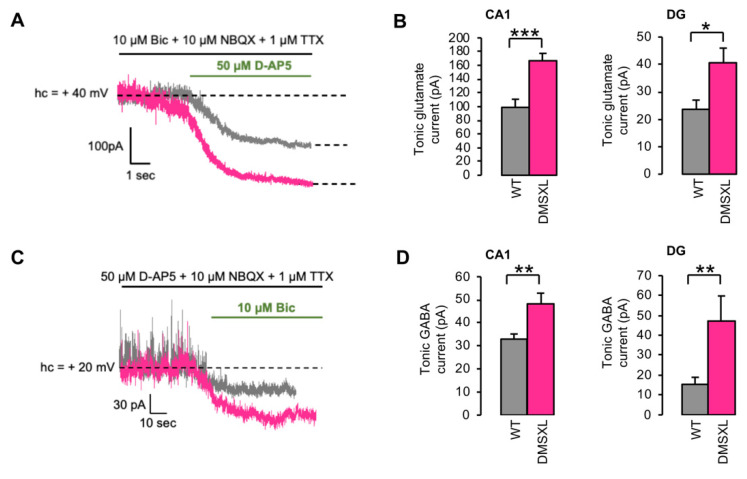
Figure 3.
Glutamate and GABA tonic currents in CA1 and DG. (A) Representative example of a glutamate NMDA-dependent tonic current, recorded at +40 mV holding potential in CA1, in WT (grey) and DMSXL (magenta) mice at 1–2 months of age. (B) The mean amplitude of tonic glutamate currents was evaluated after the action of the NMDAR antagonist D-AP5 and was statistically higher in the CA1 and DG of DMSXL mice (n = 8 mice, n = 14 neurons), compared with WT controls (n = 6 mice, n = 13 neurons). CA1, *** p = 0.0002; DG, * p = 0.012. (C) Representative example of a GABA-dependent tonic current, recorded at +20 mV holding potential in DG, in WT (grey) and DMSXL (magenta) mice at 1–2 months of age. (D) The mean amplitude of tonic GABAergic currents was evaluated after the action of the GABAA antagonist bicuculline and was significantly higher in both hippocampal areas of DMSXL mice (CA1, n = 11 mice, n = 17 neurons; DG, n = 3 mice, n = 7 neurons), relative to WT controls (CA1, n = 8 mice, n = 17 neurons; DG, n = 5 mice, n = 13 neurons). CA1, ** p = 0.0056; DG, ** p = 0.0064.