Figure 3.
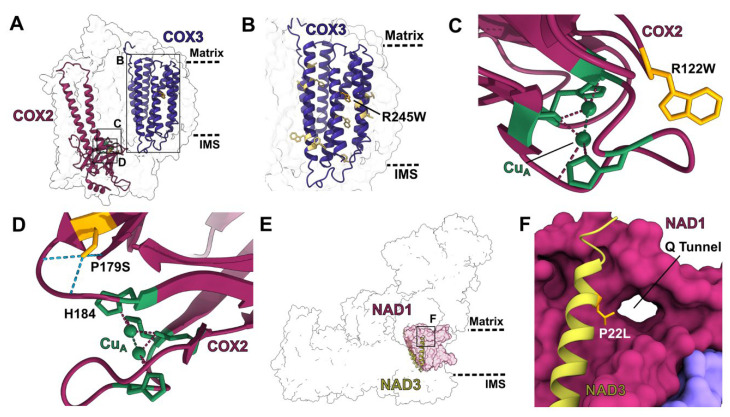
Structural characterization of edits by select multi-site PPR proteins: (A) Overall position of the edits produced by PPR protein PpPPR_77 in V. radiata complex IV (PDB: 7JRO). Edited subunits are shown in colored cartoon. Insets show the positions of panels (B–D). (B–D) Structural details of edited residues. Edited residues are shown in orange stick representation. (B) COX3′s transmembrane region (dark purple cartoon). COX3′s residue 245 is edited from arginine to tryptophan (R245W), removing a positively charged residue from the hydrophobic environment of the membrane. Other edited residues in COX3′s transmembrane region are shown in light yellow stick. Approximate location of the matrix and IMS are shown in dashed lines. (C) Copper site for electron transfer from cytochrome c (not shown) in COX2 (maroon cartoon). Copper atoms of CuA center are shown in green, with coordinating residues in green stick and coordination bonds in dashed lines. COX2′s residue 122 is edited from arginine to tryptophan (R122W). The positive charge of the arginine would alter the electronic environment of the CuA center. (D–F) Structural details of edits produced by PPR protein DEK10 in V. radiata complex IV and A. thaliana complex I. (D) CuA site of COX2 as in panel (C). DEK10 edits COX2′s residue 179 from proline to serine (P179S). Serine-19 forms multiple hydrogen bonds (light blue dashed lines) that position the loop that leads to CuA-coordinating residue histidine-184 (H184). (E) Overall position of the DEK10 edit in A. thaliana complex I (PDB: 7AR8). Edited subunit (NAD3) is shown in light green cartoon. Interaction subunit (NAD1) is shown in magenta surface. Inset shows the position of panel (F). (F) NAD3′s interface with NAD1 at the entrance of the Q tunnel, through which complex I’s substrate quinone enters its active site. DEK10 edits NAD3′s residue 22 from proline to leucine (P22L). A proline in this position would break the helix, affecting the access of quinone to the active site.