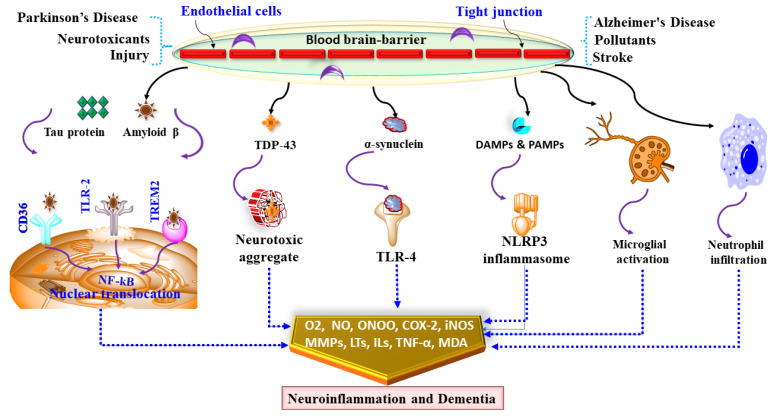
Figure 2.
Showing mediators and neuroinflammatory modulators and dementia. Coexisting neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and exposure to neurotoxic stimulus cause damage to BBB via alteration in endothelial cells and tight junctions. Damaged BBB causes NLRP3, TLR-4 and microglial activation, macrophage infiltration and nuclear translocation of NF-kB that cumulatively causes oxidative stress and neuroinflammation that leads to dementia.