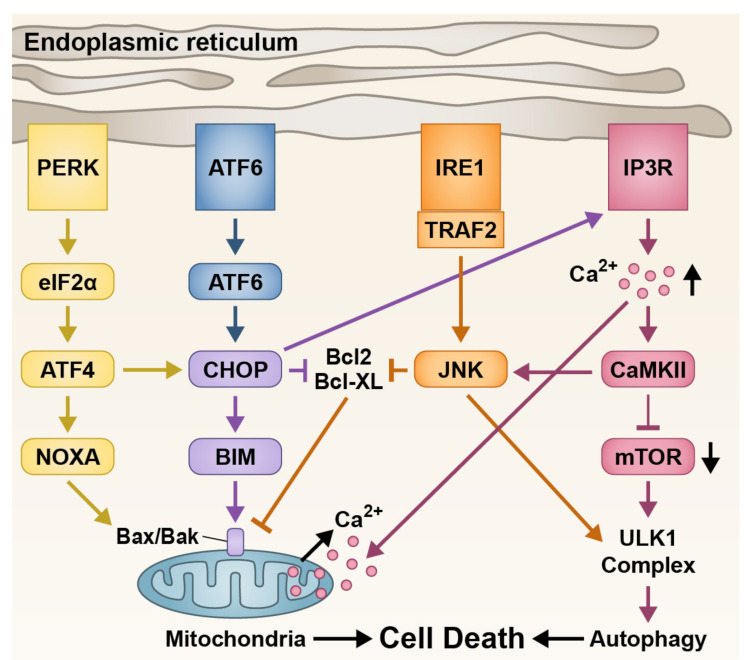
Figure 3.
ER stress pathways through activation of transmembrane ER proteins to induce cell death. PERK and ATF6 triggers CHOP activation, blocking pro-survival proteins BCL2 and BCL-XL, and inducing mitochondria-mediated cell death. CHOP can also act on IP3R to release Ca2+ from the ER, leading to further mitochondrial dysfunction and autophagy-mediated cell death. IRE1 interacts with TRAF2 to activate the JNK pathway, blocking pro-survival proteins and increasing autophagy activity. ATF4: activating transcription factor 4; ATF6: activating transcription factor 6; BAK: Bcl-2 homologous antagonist killer; BAX: Bcl-2-associated X protein; BCL2: B-cell lymphoma-2; BCL-XL: B-cell lymphoma-extra large; BIM; Bcl-2-like protein 11; CaMKII: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; CHOP: CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; eIF2α: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α; IP3R: inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor; IRE1: inositol-requiring enzyme 1; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; mTOR; mammalian target of rapamycin; NOXA: phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetated-induced protein 1, also known as (PMAIP1); PERK: protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; TRAF2: TNFR1-associated factor 2; ULK1: Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1.