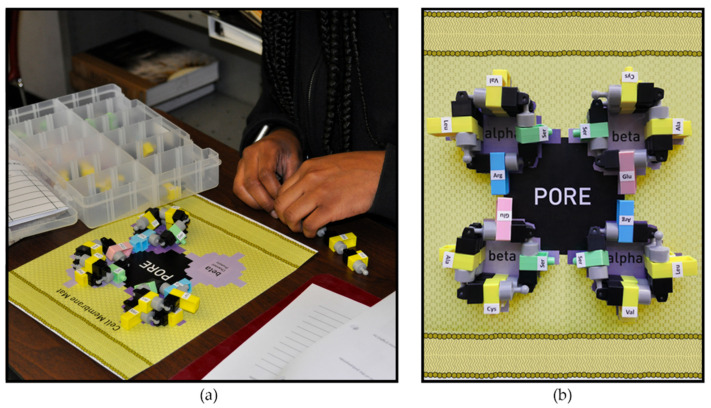
Figure 4.
Channel protein model assembly on the cell membrane mat. (a) Participants assemble amino acids into a protein chain, following a specific sequence and fold the chain into an alpha helix with the side chains (-R groups) pointing toward the outside of the helices. (b) Top-down view of a cell membrane model with a functional channel protein represented by four amino acid chains in four helices spanning the cell membrane. This pore is functional because the hydrophilic amino acids face towards the interior of the pore, expediting the passage of ions through the cell membrane. The hydrophobic amino acids in the helices all face the hydrophobic lipids in the surrounding cell membrane. The protein’s function depends upon the order of the amino acids in the chain.