Fig. 3: GluD1 transduces both the NRXN1SS4+ signal that enhances NMDAR EPSCs and the NRXN3SS4+ signal that suppresses AMPAR EPSCs.
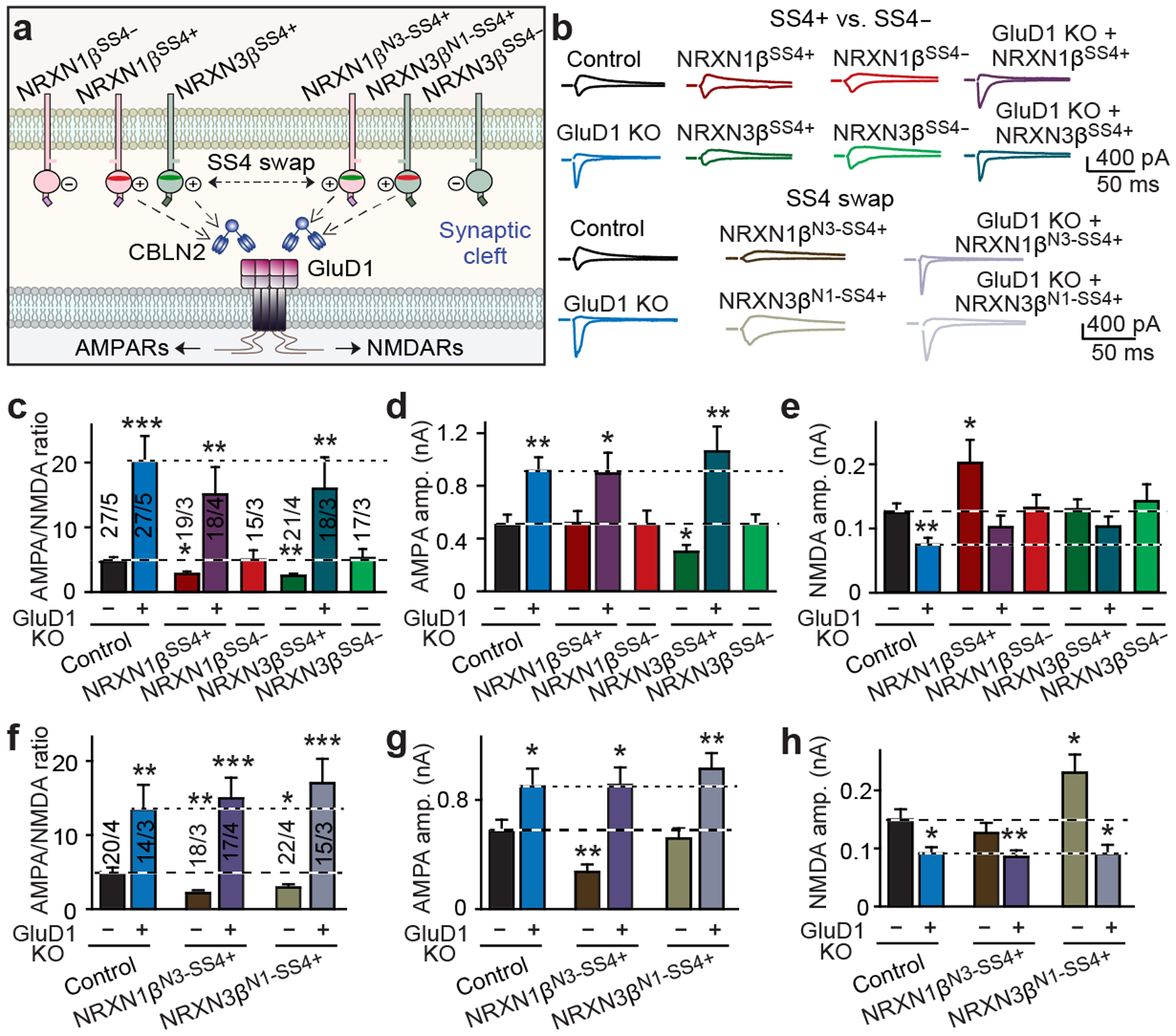
a, Schematic of NRXN1β–CBLN2–GluD1 and NRXN3β–CBLN2–GluD1 signalling pathways. b, Representative AMPAR-EPSC and NMDAR-EPSC traces from cultured hippocampal neurons. c–e, After deletion of GluD1, NRXN1βSS4+ and NRXN3βSS4+ do not decrease the AMPA/NMDA EPSC ratio (c), NRXN3βSS4+ does not suppress AMPAR ESPCs (d) and NRXN1βSS4+ does not enhance NMDAR EPSCs (e). f–h, The SS4 sequences of NRXN1SS4+ and NRXN3SS4+ determine their functional specificity. f, AMPA/NMDA EPSC ratios. g, AMPAR EPSCs. h, NMDAR EPSCs. Data are mean ± s.e.m. Numbers of neurons/independent experiments are indicated in bars. Statistical significance was assessed by two-tailed Student’s t-test, comparing to control. Exact P values are presented in the Source Data.
