Extended Data Fig. 1. CRISPR-mediated deletion and synaptic localization of GluD1 in cultured hippocampal neurons, and the effect on synapse numbers and synaptic function.
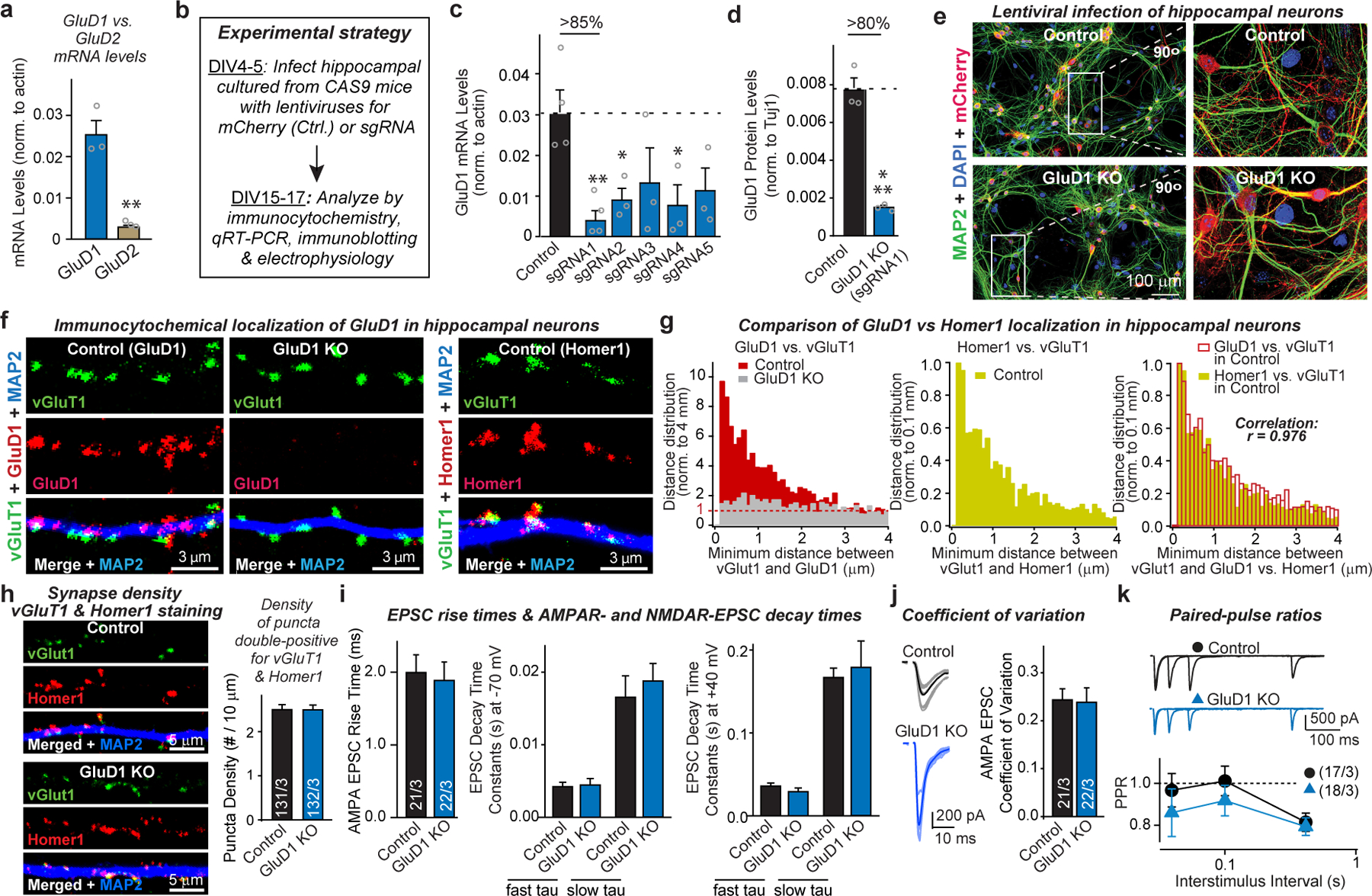
a, Quantitative RT–PCR demonstrating robust GluD1 but weak GluD2 expression in cultured hippocampal neurons, providing the rationale for targeting GluD1 over GluD2. b, Experimental strategy for the CRISPR-mediated GluD1 deletion. Hippocampal cultures from Cas9-expressing transgenic18 mice were infected at DIV4–5 with lentiviruses expressing only mCherry or co-expressing mCherry with GluD1-directed sgRNAs, and were analysed at DIV15–17. c, Screening of five sgRNAs for the GluD1 KO efficacy in hippocampal cultures from Cas9-expressing transgenic mice18. GluD1 mRNA levels were analysed by quantitative RT–PCR in neurons as described in a. sgRNA sequences: sgRNA1, 5′-GCCGACTCCATCATCCACAT-3′; sgRNA2, 5′-GTAACGCACTGGCATATCCA-3′; sgRNA3, 5′-GGCCAATAATCCGTTCCAGG-3′; sgRNA4, 5′-GAACGCAGCCAAGGACGACA-3′; sgRNA5, 5′-CTTCGAGGAGAACGCAGCCA-3′. sgRNA1 was used for all subsequent experiments. d, GluD1 deletion using sgRNA1 in hippocampal cultures from Cas9-expressing transgenic mice abolishes most GluD1 protein expression by the time of analysis used in the current experiments. Protein levels were quantified using immunoblots (see Fig. 1b) with fluorescent secondary antibodies. e, Representative images of more than 3 experiments of hippocampal neurons cultured from Cas9-expressing transgenic mice and infected with a control lentivirus or a lentivirus expressing sgRNA1 targeting GluD1 (CRISPR). Neurons were stained for MAP2 and DAPI; the mCherry signal is from the lentiviruses). f, Representative images of hippocampal neurons cultured from Cas9-expressing transgenic mice and infected with a control lentivirus or a lentivirus expressing sgRNA1 targeting GluD1 (CRISPR, used as a negative control for GluD1 staining). Neurons were stained for vGluT1, MAP2 and GluD1 (left and middle panels) or Homer1 (right panels). g, Co-localization quantifications indicate that the GluD1 and the Homer1 signals are both adjacent to vGluT1 signals and are highly correlated with each other (Pearson correlation test). For minimum distance quantification, the range of 0.1–4 μm was analysed for distances between presynaptic vGlut1 and postsynaptic GluD1 or Homer1. h, CRISPR-mediated deletion of GluD1 has no effect on excitatory synapse numbers in hippocampal neurons, independently confirming the experiments shown in Fig. 1 using double labelling for pre- and postsynaptic excitatory synapse markers (vGluT1 and Homer1, respectively). Only puncta positive for both markers were quantified (left, representative images of neurons stained for vGluT1, Homer1 and MAP2; right, summary graphs of the density of double-positive for vGluT1 and Homer1 synaptic puncta). i, CRISPR-mediated GluD1 deletion does not alter EPSC kinetics (left, AMPAR-EPSC rise time (20–80%); middle, AMPAR-EPSC decay constants at −70 mV fitted with double-exponential function; NMDAR-EPSC decay constants at +40 mV fitted with double-exponential function. Data for i and j are from the experiments of Fig. 1g–i. j, k, CRISPR-mediated GluD1 deletion does not alter the coefficient of variation (j; left, representative traces; right, summary graph of coefficient of variation), or the PPR of AMPAR-EPSCs (k; top, sample traces; bottom, summary plots of the PPRs as a function of interstimulus intervals (ISIs)). Data are means ± s.e.m. (number of independent experiments (data points) is indicated in the bars of a–d, regions of interests/independent experiments is listed in h, and number of neurons/ independent experiments is indicated in i–k). Statistical significance was assessed by two-tailed Student’s t-test or two-way ANOVA (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001; for numerical P values, see source data; non-significant comparisons are not indicated).
