FIGURE 4.
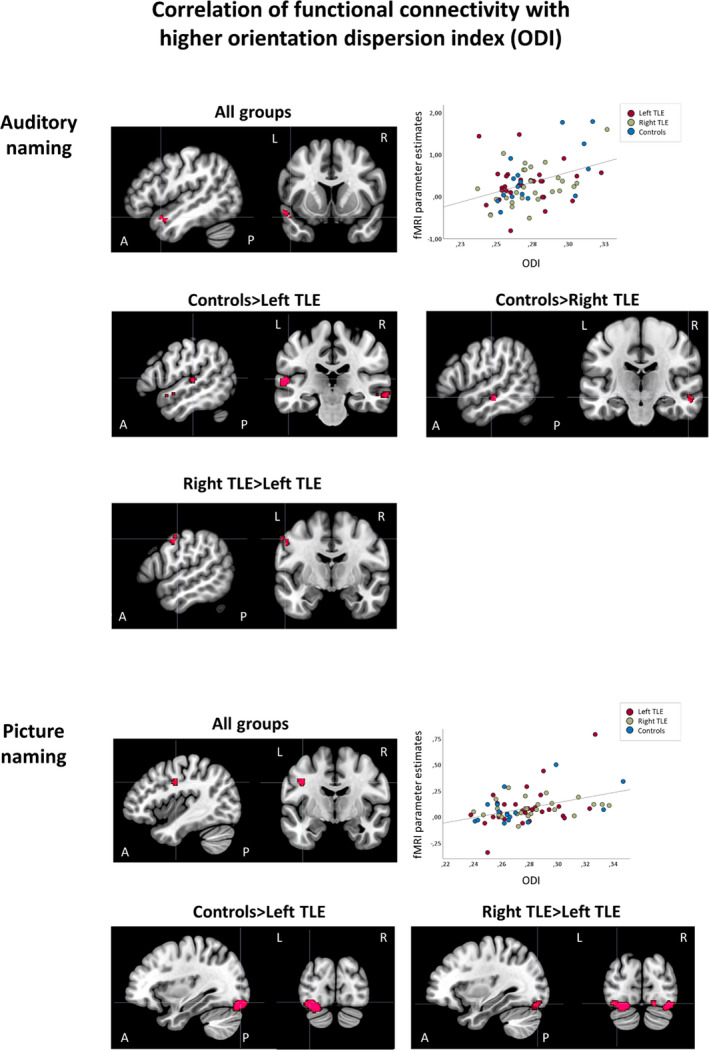
Correlations of functional connectivity of auditory naming (seed region: left inferior temporal gyrus) and picture naming (seed region: left fusiform gyrus) with higher orientation dispersion index (ODI) of underlying white matter tracts. Areas of significant connectivity are shown superimposed on sagittal and coronal T1 images masked for the group effects at p < .001 uncorrected. Top three rows: Auditory naming. Stronger functional connectivity correlated with higher ODI in the left anterior superior temporal gyrus in all groups. Scatterplot shows correlation of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) parameter estimates extracted from the left anterior superior temporal gyrus with mean ODI values. Controls had stronger correlations compared to both left temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE; bilateral anterior superior and middle temporal gyrus) and right TLE (right anterior superior temporal gyrus). Bottom two rows: Picture naming. Across groups, correlation of stronger functional connectivity with higher ODI was seen in the left precentral gyrus. Scatterplot shows correlation of fMRI parameter estimates extracted from the left precentral gyrus with mean ODI values. Compared to left TLE, stronger correlations were seen in controls (bilateral lingual gyrus, left cerebellum) and right TLE (bilateral lingual gyrus, left cerebellum, right fusiform gyrus). A, anterior; L, left; P, posterior; R, right
