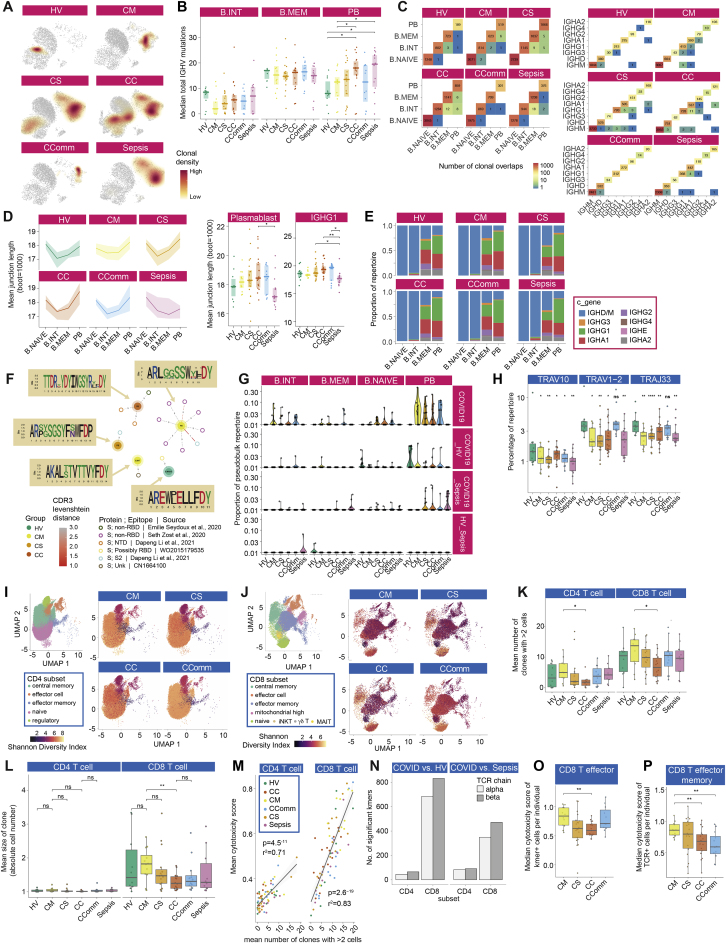
Figure S7.
Differences in B and T cell repertoire associated with COVID-19 severity, related to Figure 5
(A-G) Analysis of B cell immune repertoire using bulk VDJ sequencing of whole blood (1,206,531 filtered BCR sequences analyzed) and single cells (CITE-seq). (A) Clonal density plots with Kernels density estimates overlaid onto UMAP embeddings by comparator group. (B) IGHV total mutations across B cell subsets per study group (naive B cells not shown, as no mutations). (C) Clonal overlaps across B cell clusters and across constant region genes per study group. Numbers reflect binary detection events mutation and expansion proportions in plasmablast clone repertoire. (D) Junction lengths from resampled repertoires by patient group per B cell cluster and in plasmablasts and in plasmablast immunoglobulin constant gene IGHG1. The line shows mean amino acid junction length; the ribbon range is the 0.25-0.75 quantiles of bootstrapped samplings. (E) Ig constant region genes per B cell cluster (single cell VDJ data). (F) Sequence similarity network of VDJ sequences, from single cell VDJ data (central nodes), to published monoclonal antibodies (peripheral nodes; references and epitopes described in legend). Edges depict pairwise Levenshtein’s distance of CDR3s. CDR3 sequence logos are shown following multiple sequence alignment. (G) The proportion of B cells across each B cell cluster per disease group of sequences shared between patient groups (observed in at least 2 patients). (H-P) Analysis of T cell immune repertoire. (H) TRAV and TRAJ repertoire analysis. (I,J) UMAP of CD4+ T cells (I) and CD8+ T cells (J) with associated clusters used in repertoire analysis indicating Shannon Diversity Index by patent group. For clusters used in repertoire analysis see Data S3. (K) Number of enlarged clones by comparator group in CD4+ and CD8+ subsets. (L) Mean clone size CD4 and CD8. (M) Using a pre-defined cytotoxicity metric the overall cytotoxicity was calculated per individual for both the CD4+ and CD8+ subsets. For each individual the number of enlarged clones in these subsets was determined (defined as > 2 cells with the same TCR chain). Mean cytotoxicity per individual is correlated with the number of expanded clones across each individual, irrespective of cohort origin (Pearson’s r2). For illustration of the method used to identify CDR3 Kmers associated with COVID-19 compared to cells from healthy volunteers and patients with sepsis see Data S3. (N) Number of Kmers comparing COVID-19 versus healthy volunteers and sepsis. (O) Cytotoxicity of CD8+ T effector cells positive for a COVID-19 associated Kmer across patient groups. (P) Cytotoxicity of CD8+ T effector memory cells with clonotypes matching published COVID-19 clonotypes. Comparator group abbreviations. HV: healthy volunteer; CM: COVID-19 in-patient mild; CS: COVID-19 in-patient severe; CC: COVID-19 in-patient critical; CComm: COVID-19 community case in the recovery phase (never admitted to hospital); Sepsis: in-patient severe and critical sepsis. Wilcoxon Test age and sample size adjusted linear model used ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. All boxplots show median, first and third quartiles; whiskers show 1.5x interquartile range.