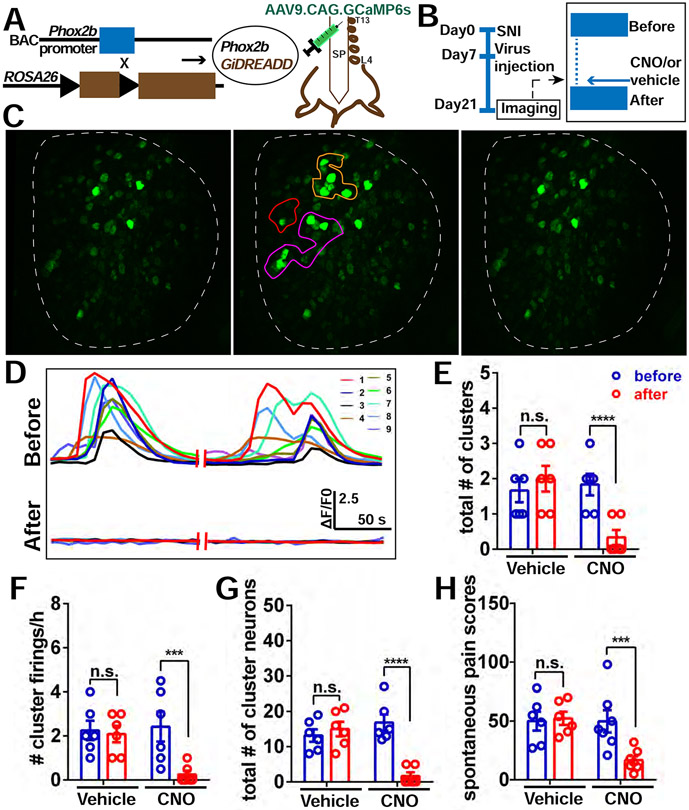
Figure 4. Chemogenetic silencing of sympathetic nerve activity in the DRG diminishes the incidence of CFEs and relieves spontaneous pain.
(A) Diagram showing the mating strategy and intrathecal injection with AAV9.CAG.GCaMP6s in Phox2bCre; GiDREADD mice.
(B) Diagram showing the experimental procedure. On POD 21, in vivo imaging of L4 DRG was first recorded for 2 hours followed by topical application of 10 μM CNO or vehicle (0.1%DMSO) on the surface of the DRG to locally activate the DREADD receptors in sympathetic nerves. In vivo imaging was then resumed for an additional 2 hours.
(C) An example of decreased cluster firing after local addition of CNO on the DRG. Left is quiescent (i.e. period with no cluster firing); Middle is an example of cluster firing before CNO addition. There are 3 clusters (orange, purple and red circles). Right is after CNO addition, all 3 clusters were diminished.
(D) Representative traces of neurons in the orange cluster which are numbered in (C) before and after administration of CNO.
(E-G) The total number of clusters (E), frequency of cluster firing (F), and total number of cluster firing neurons (G) is significantly inhibited after addition of CNO to DRG, but not with addition of vehicle (0.1% DMSO in saline).
(H) Spontaneous pain scores significantly decreased after i.t. administration of CNO in SNI mice (Day 20) with cluster firing. No change was observed with administration of vehicle.
Scale bar, 100 μm. Each pair of open circles (before and after) represents an individual mouse. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; n.s., not significant; (E) to (H) by two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Sidak’s posttest.