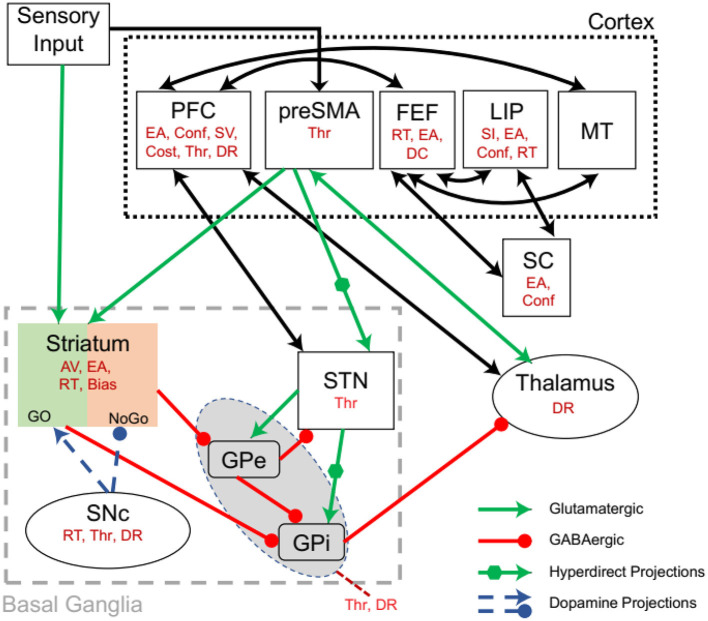
Figure 2.
Interactions between the cortico-basal ganglia system showing the effect of an area on DDM parameters (in red). Based on the sensory inputs, the pre-supplementary motor area (pre-SMA) determines competing motor commands. Together sensory and pre-SMA inputs are projected to the striatum (STR). The pre-SMA also projects to subthalamic nucleus (STN) via a hyperdirect pathway. The action of dopamine from SNc modulates the Go and No-Go neurons in the STR. STR inhibits globus pallidus externa (GPe), which in turn inhibits globus pallidus interna (GPi). STR also inhibits GPi and STN has hyperdirect projections to GPi. GPi inhibits the thalamus. The STR-GPi pathways have an overall disinhibiting effect on the thalamus, while the STR-GPe-GPi has an overall inhibitory effect on the thalamus. PFC, Prefrontal Cortex; preSMA, pre-supplementary motor area; FEF, Frontal eye field; LIP, Lateral intraparietal area; MT, Middle temporal area; EA, Evidence accumulation; Conf, Confidence; SV, Stimulus valuation; Thr, Threshold; DR, Drift rate; AV, Action valuation; RT, Reaction time; selection; DC, Decision commitment; SI, Stimulus identity. Modified from Ratcliff and Frank (2012).