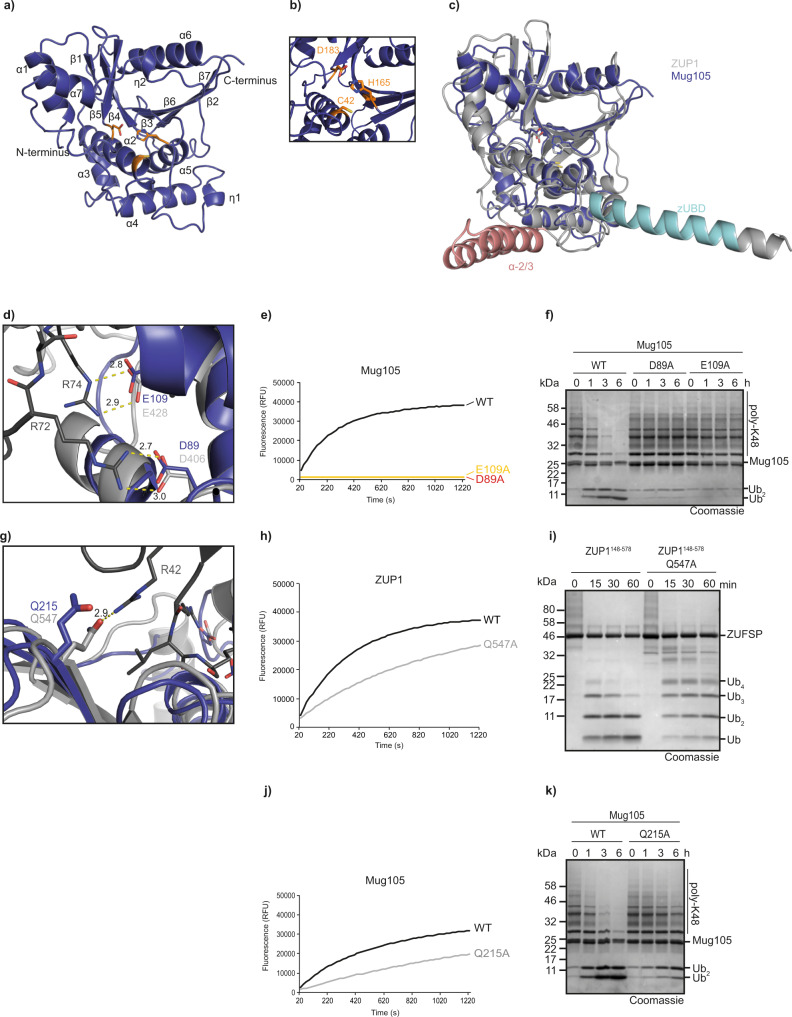
Fig. 1. Crystal structure of ZUFSP family member Mug105.
a Overview of the crystal structure in cartoon representation. The catalytic core of Mug105 is shown in blue. The catalytic triad is shown as orange sticks. b Magnification of the active site of Mug105 (blue). The catalytic triad is shown as orange sticks. c Structural superposition of Mug105 (blue) and ZUP1 (6EI1, gray). The RMS distance is 1.7 Å over 215 residues. The characteristic helical protrusions of ZUP1 are colored cyan (zUBD) and red (α-2/3). d Recognition of ubiquitin C terminus by the catalytic core of Mug105. Mug105 (blue) and the ZUP1(light gray)/ubiquitin (dark gray) complex are superimposed and shown in cartoon representation. Key residues are highlighted as sticks. Salt bridges are indicated by dotted lines. e Activity of C-terminus recognition mutants (Mug105 D89A or E109A) against RLRGG-AMC. The RFU values shown are the means of triplicates. f Activity of mutants described in e against K48-linked ubiquitin chains. g Recognition of ubiquitin Arg-42. ZUP1 Gln-547 (light gray) forms a hydrogen bond (indicated by yellow dotted line) with ubiquitin Arg-42 (dark gray). The superimposed Gln-215 of Mug105 is conserved and also able to form a hydrogen bond with ubiquitin Arg-42. h, j Activity of mutants ZUP1148–578 Q547A (h) or Mug105 Q215A (j) against RLRGG-AMC. The RFU values shown are the means of triplicates. i Activity of ZUP1148–578 Q547A against K63-linked ubiquitin chains. k Activity of Mug105 Q215A against K48-linked ubiquitin chains. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.