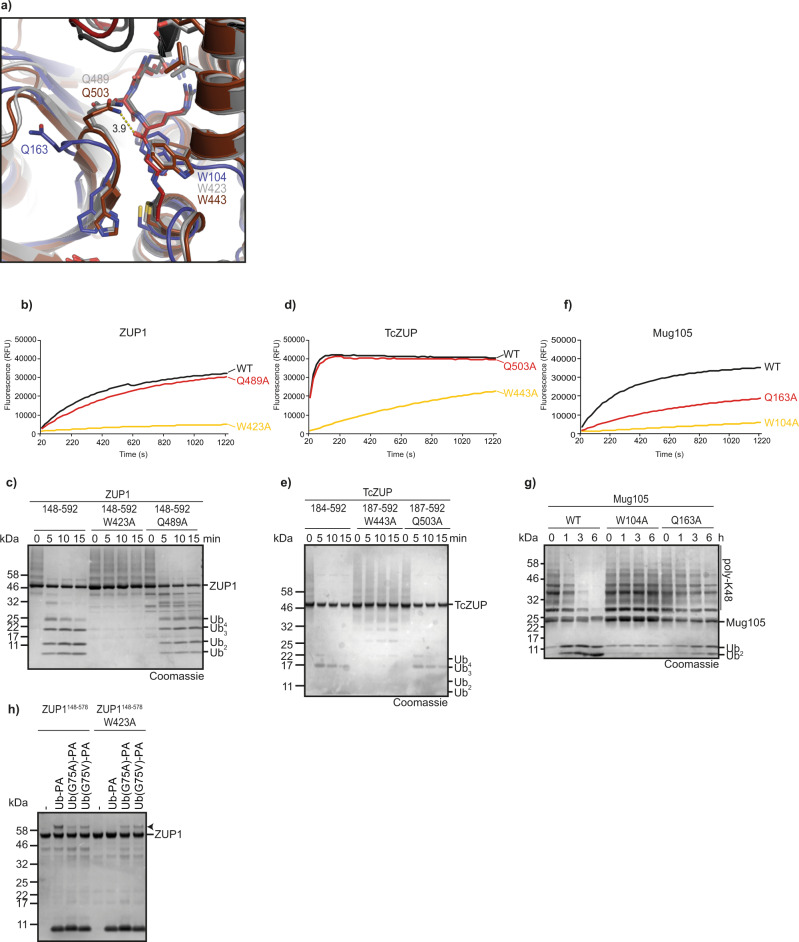
Fig. 5. Ubiquitin-binding induced conformational changes.
a Structural superposition of ubiquitin-bound TcZUP (brown) and ZUP1 (6EI1, gray) with ubiquitin-less Mug105 (blue). The catalytic core is shown in carton representation and key residues are highlighted as sticks. C-terminal residues of ubiquitin are shown as sticks and colored red and dark gray. Trp-104 and Gln-163 exhibit different conformations compared to the corresponding residues of ZUP1 and TcZUP. b, c Activity of ZUP1148–578 W423A or Q489A against RLRGG-AMC (b) or K63-linked Ub6+ chains (c). d, e Activity of TcZUP187–592 W443A or Q503A against RLRGG-AMC (d) or K63-linked Ub6+ chains (e). f, g Activity of Mug105 W104A or Q163A against RLRGG-AMC (f) or K48-linked ubiquitin chains (g). h Activity-based probe reaction of wildtype or W423A-mutated ZUP1148–578 with Ub-PA. Both DUBs were tested against WT, G75A, or G75V Ub-PA. Black arrowheads mark the shifted band after reaction. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.