Fig. 5. Metabolic reconstruction of active ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in response to agricultural reclamation of Solonetz saline-sodic soil.
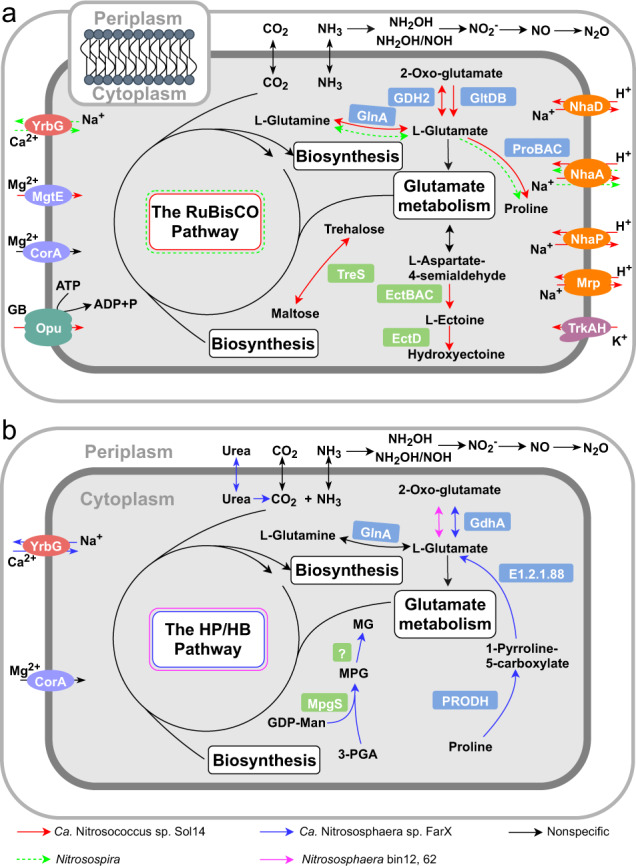
Cell metabolism diagrams of AOB (a) and AOA (b) were constructed from the genome annotation of Ca. Nitrosococcus sp. Sol14, Ca. Nitrososphaera sp. FarX and Nitrososphaera bin12, 62 and the scaffold annotation of the genus Nitrosospira. Putative adaptations to high salinity and selected core metabolic pathways of ammonia oxidizers are shown. NhaA NhaA Na+/H+ antiporter, NhaD NhaD Na+/H+ antiporter, NhaP NhaP Na+/H+ antiporter, Mrp Mrp Na+/H+ antiporter, Trk Trk K+ uptake system, MgtE/CorA magnesium uptake mediated by facilitated diffusion, Opu glycine betaine uptake transporter, TreS trehalose synthase, EctA diaminobutyrate acetyl transferase, EctB diaminobutyrate transaminase, EctC ectoine synthase, EctD ectoine hydroxylase, GDH2 and GdhA glutamate dehydrogenase, GlnA glutamine synthetase, GltDB glutamate synthase, ProA glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, ProB glutamate-5-kinase, ProC pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase, YrbG Ca2+/Na+ antiporters, PRODH proline dehydrogenase, E1.2.1.88 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase, MpgS mannosyl-3-phosphoglycerate synthase, question mark (?) uncharacterized phosphatase, GB glycine betaine. See Table S7 for detailed gene presence/absence.
