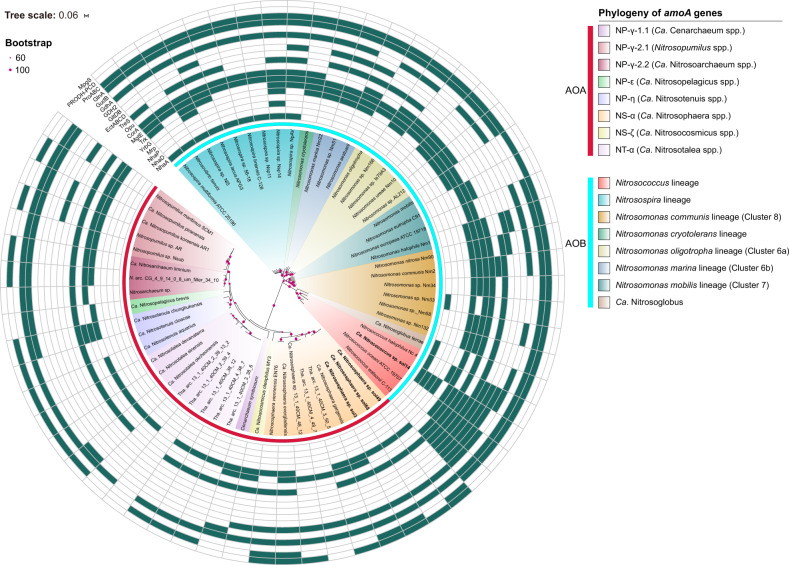
Fig. 6. Meta-analysis of salt resistance genes in phylogenetically distinct ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea.
Phylogenetic tree of amoA genes from typical AOA and AOB species, with known genomes (see Table S6), including those from the MAGs in this study, highlighted in bold. Representative amoA sequences were phylogenetically analyzed with MEGA version 7.0 using the neighbor-joining method and the maximum composite likelihood model with 1000 replicates to generate bootstrap values. Outside the tree, the phylogenetic grouping of AOA and AOB is shown in the first internal ring with the colored strip in red and blue, respectively. The salt tolerance proteins identified in active ammonia oxidizers in this study (Fig. 5) are shown from the internal 2nd ring to the 20th ring including those encoding proteins of NhaA; NhaD; NhaP; Mrp; YrbG; Trk; MgtE; CorA; Opu; TreS; EctABCD; GltDB; GDH2; GdhA; GudB; GlnA; ProABC; PRODH-PCD; and MpgS. The presence and absence of these proteins in ammonia oxidizers are indicated in green and white, respectively. GudB, glutamate dehydrogenase (K00260); PCD, E1.2.1.88/1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase.