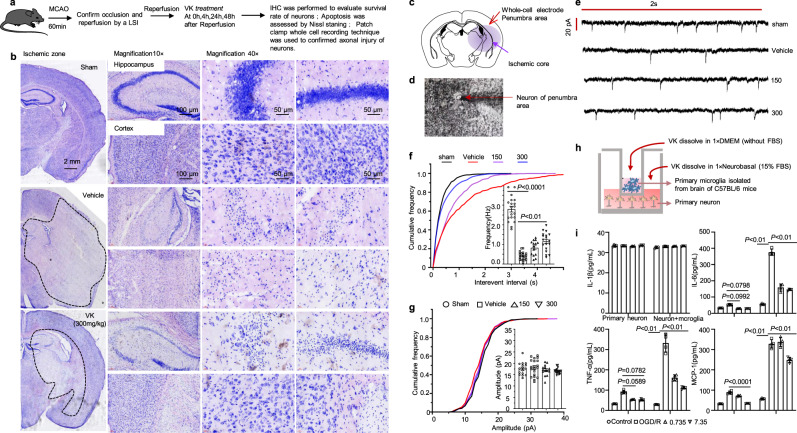
Fig. 6. VK protects neurons against cell death and axonal injury in stroke mice.
a Experimental design: in addition to the sham group, mice (8–10 weeks, male) were subjected to MCAO for 60 min. Mice were randomized into four groups: sham group, vehicle group, VK (150 and 300 µg/kg) groups. Mice were administered VK at 0, 4, 24, and 48 h after MCAO/R as assessed cell death and axonal injury by IHC staining for NeuN+, Nissl staining, and patch-clamp whole-cell recording. b Nissl staining for the mice hippocampus (CA1 region, interaural: 2.10–2.58 mm, bregma −1.46 to −1.22 mm) and cortex in each group was displayed. Position of stimulating and recording electrodes for conduction velocity measurements in (c, d). e Representative firing patterns of pyramidal neurons from mouse neocortex elicited by depolarizing current steps after MCAO/R. All miniature excitatory post synaptic currents (mEPSCs) were recorded at a holding potential of −65 mV. f Cumulative frequency plots of the interevent interval (left) and quantitative analysis of the frequency of AMPA receptor-mediated mEPSCs (right). g Cumulative frequency plots of the amplitude (left) and quantitative analysis of the amplitude of AMPA receptor-mediated mEPSCs (right). Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, n = 5–7. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni test as post-hoc comparisons. h Schematic showing that primary cortical neurons obtained from fetal C57BL/6 mice of embryonic day 16–17.5 and primary microglia isolated from C57BL/6 mice at postnatal day 1–2 were co-cultured with or without VK. For the co-culture system, (i) cell supernatant was collected to measure proinflammatory factors. Data are mean ± SD (n = 4).