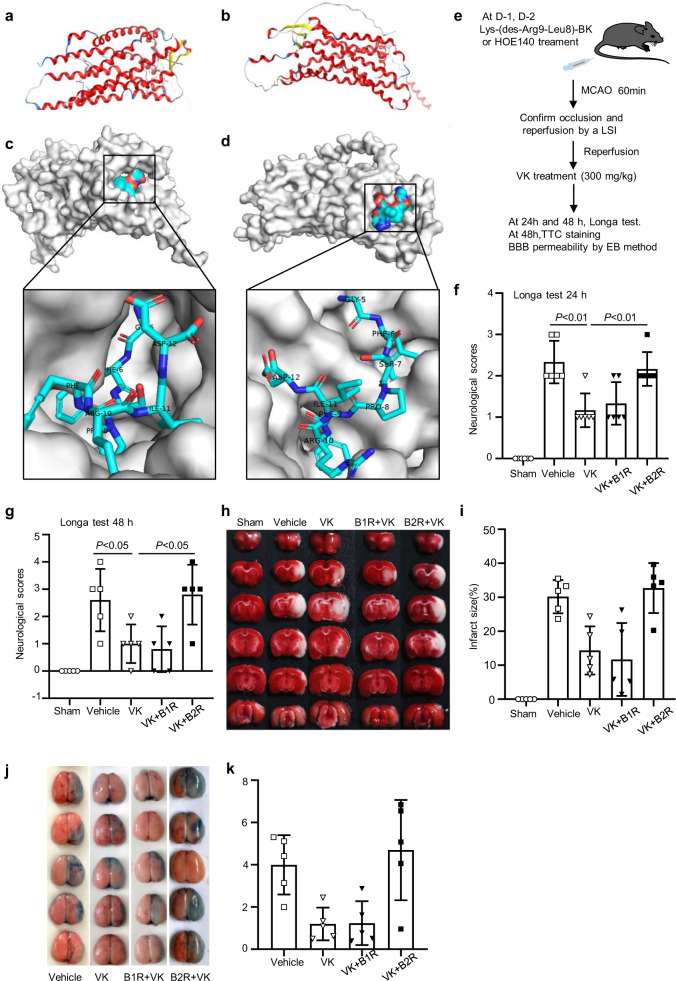
Fig. 8. VK-B1R or B2R interaction and the effect of B1R antagonist or B2R antagonist on stroke in mice.
a Secondary structure of the B1R predicted by AlphaFold (ID: AF-Q61125-F1). b The peptide docking model of VK and B1R with the highest score. c Secondary structure of the B2R predicted by AlphaFold (ID: AF-P32299-F1). α helixes, β sheets, and loops were depicted in red, yellow, and blue, respectively. d The peptide docking model of VK and B2R with the highest score (performed by online HDOCK SERVER: http://hdock.phys.hust.edu.cn/). e Experimental design: Mice (8–10 weeks, male) were randomized into five groups: sham group, vehicle group, VK (300 µg/kg) group, B1R antagonist + VK group, and B2R antagonist + VK group. The B1R + VK and B2R + VK groups were administrated Lys-(des-Arg9-Leu8)-BK and HOE140, respectively, before MCAO-induced stroke. In addition to the sham group, all mice were subjected to MCAO for 60 min. Mice were administered by VK at 0, 4, 24, and 48 h after MCAO/R and the stroke outcomes were assessed by Longa test, TTC staining, and Evans blue (EB) method. f, g The inhibitors affected neurological function following MCAO using the Longa test. h TTC staining of representative coronal sections at 48 h after reperfusion. i Quantitative analysis of infarct size at 48 h after MCAO/R. j Representative coronal brain sections showing EB extravasation. k EB extravasation was detected by fluorescence spectrophotometry. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 5–6. Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Tukey multiple comparisons test.