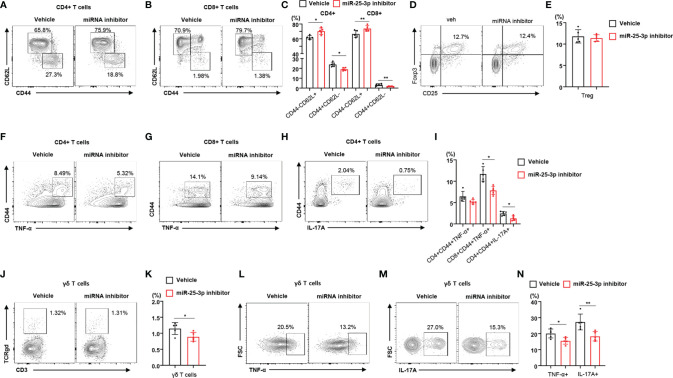
Figure 3.
Inhibition of miR-25-3p attenuates periodontal inflammation in male mice with diet-induced obesity and periodontitis. (A–C) Representative flow cytometry plots and percentages of CD44+CD62L− and CD44−CD62L− cells in the CD4+ and CD8+ T cell populations from submandibular lymph nodes of either vehicle-treated (n = 5) or miR-25-3p inhibitor-treated (n = 5) male mice with periodontitis 9 days after ligature placement. (D, E) Representative flow cytometry plots and frequencies of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in HFD-fed mice treated with either miR-25-3p inhibitor or vehicle. (F–I) Percentages of TNF-α- or IL-17A-producing cells in the population of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells in periodontitis-induced mice treated with either miR-25-3p inhibitor or vehicle. (J, K) Percentages of γδ T cells in submandibular lymph nodes of periodontitis-induced mice treated with either miR-25-3p inhibitor or vehicle. (L–N) Representative flow cytometry plots and percentages of TNF-α- or IL-17A-producing cells in the population of γδ T cells from periodontitis-induced mice treated with either miR-25-3p inhibitor or vehicle. Data represent mean values of more than three independent experiments. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (C, E, I, K, N), two‐tailed t tests.