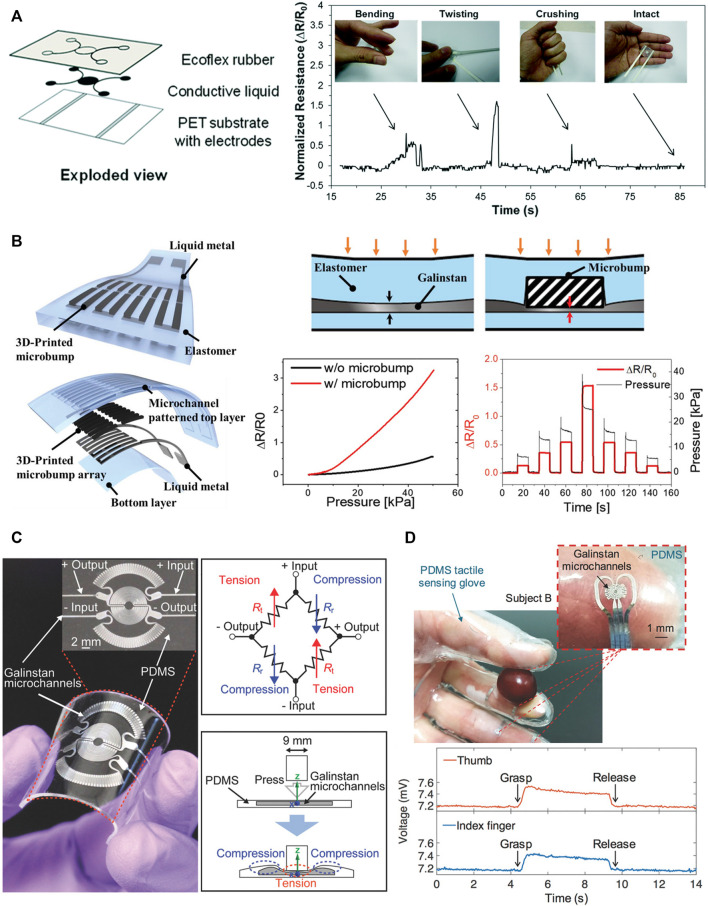
FIGURE 5.
Microfluidic tactile sensing based on electrical resistance change. (A) Exploded view of the flexible microfluidic pressure sensor and normalized electrical resistance profile of the pressure sensor subjected to bending, twisting, and crushing during characterization (Yeo et al., 2016b). Published by The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC). (B) Schematic of the 3D‐printed rigid microbump‐integrated liquid metal‐based pressure sensor showing the effect of the microbump on pressure sensitivity and the sensing response to the application of varying pressure levels (Kim et al., 2019). Copyright (2019) WILEY-VCH. (C) Optical image and schematics of a microfluidic tactile diaphragm pressure sensor with liquid metal Wheatstone bridge circuit. (D) Real-time response recorded from the corresponding thumb and index finger sensors while grasping a grape (Gao et al., 2017). Copyright (2017) WILEY-VCH.