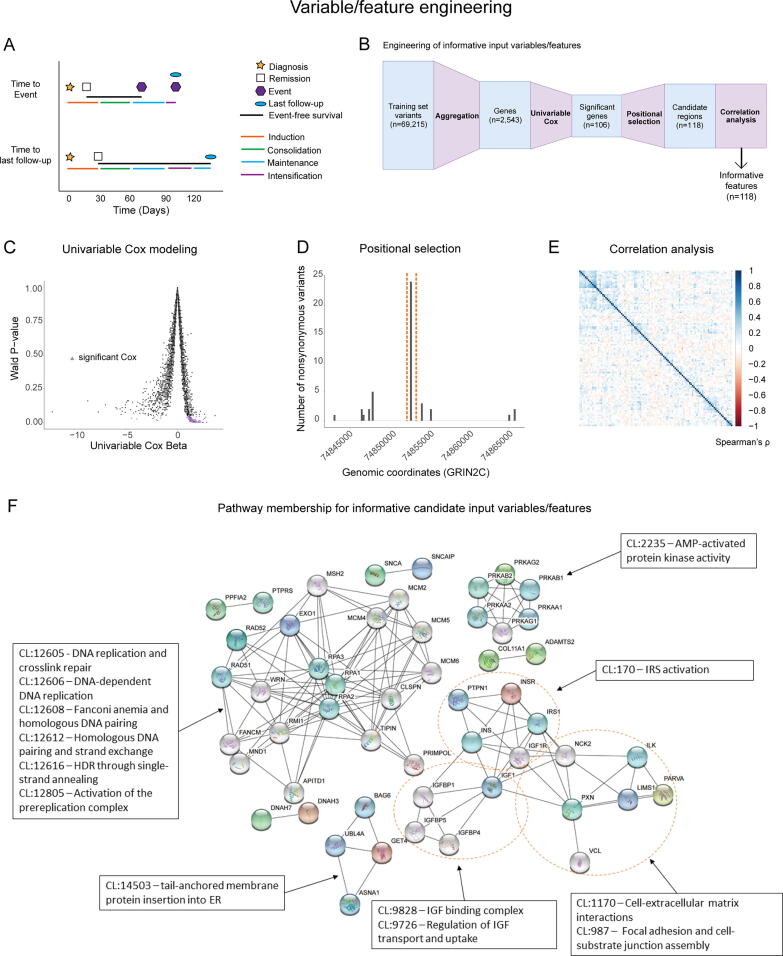
Fig. 2.
Feature selection/engineering against training cohort variants produces a reduced feature space of non-correlated variables. (A) Schematic illustrating common EFS scenarios. EFS is considered as the time from clinical remission to the time of first event or last follow-up. Events and last follow-up could occur in any treatment phase after remission. (B) Schematic illustrating the steps used for variable selection/engineering. (C) Scatter plot of univariable Cox beta values as a function of Wald P-values, where Cox estimated ability of each variable to predict EFS. Selected variables are represented by purple triangles. (D) Example of positional selection approach in the gene GRIN2C. A single hotspot region contained > 60% of all variants found in GRIN2C in this dataset, and that region was selected. (E) Correlogram showing low Spearman’s ρ values for all variables used in this study. (F) STRING cluster membership and interactions among selected variables. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)